Let’s cut to the chase: Each person working from home needs at least 100Mbps in download speed and 20Mbps in upload speed. That will be plenty of speed for video calls, streaming, handling large files, and even running a VPN.
That’s a good rule of thumb, but you may be able to get away with less. Browsing requires just about 5Mbps of speed, and most video apps require only about 20Mbps each, at any given time. It all depends on what you’re doing online, how many connected devices share a connection, whether you’re hardwired via Ethernet, and more.
Fiber, cable, and 5G home internet is fast enough for most remote work, but avoid using hotspots, DSL, or satellite internet if you can.
Do you have the speed you need to work from home?
Find out how much speed you’re getting on your current internet connection so you can decide whether it’s time to upgrade.
Download speed
000 Mbps
Upload speed
000 Mbps
Latency (ping)
00 ms
Jitter
00 ms
On this page:
Best internet providers | Video conferencing | Email and chat | Web browsing | Streaming| File sharing | What else affects internet speed | How to improve internet speed | FAQ
On this page:
Choose fiber internet for remote work
Fiber internet providers like AT&T, Google Fiber, and Verizon are the best for working from home. You get equally fast upload and download speeds, which are especially great if you need to transfer large files to a remote server or be on video calls.
We recommend starting with the cheapest (and slowest) plans from any fiber provider, and upgrading only if you run into bandwidth issues.
| Fiber Provider | Speeds up to |
|---|---|
| Astound | 5,000Mbps |
| AT&T Fiber | 5,000Mbps |
| Brightspeed Fiber | 8,000Mbps |
| CenturyLink | 940Mbps |
| EarthLink | 5,000Mbps |
| Frontier | 7,000Mbps |
| Google Fiber | 8,000Mbps |
| Optimum | 8,000Mbps |
| T-Mobile Home Internet | 2,000Mbps |
| Verizon Fios | 2,300Mbps |
| Ziply Fiber | 52,119Mbps |
Choose the highest-rated provider in your area
Your choice of internet providers is limited by your address. Not many households can actually get it, but Google Fiber was the best fiber internet provider of 2025 in overall satisfaction, reliability, and customer feedback. Regional provider Brightspeed Internet was even faster in actual recorded speeds, though, and big players T-Mobile, Verizon and AT&T generally hover in the top half of every category.
Meanwhile, you can get fiber internet from T-Mobile in a few areas, or try 5G home internet from T-Mobile in nearly 60% of areas tracked by the Federal Communications Commission. With fiber speeds up to 2,000Mbps and 5G speeds up to 415Mbps, it’s a great option for remote workers.
Get Your Internet Speed Recommendation
Est. time: 60 seconds
Answer 6 questions and get your personalized results!
How many people in your household use the internet/WiFi on a daily basis?
How many devices in your home connect to the internet, including tablets, gaming consoles, and smart devices?
How many people in your household work from home?
What video quality do you use for streaming TV and movies?
How intensely does your household participate in online gaming?
Does your household download large files from the cloud or via the internet?
Cable internet is a fast, reliable option for working from home
If you can’t get fiber internet, cable is the next best option for working from home. Download speeds range from 25–2,100Mbps, but for now, upload speeds are slower than what you get with fiber internet. For instance, your cable plan may support download speeds of up to 400Mbps, but the upload max may be 30Mbps.
Here is a list of cable internet providers for working from home:
| Cable Provider | Speeds up to |
|---|---|
| Astound | 2,000Mbps |
| Buckeye | 600Mbps |
| Cox | 2,000Mbps |
| Mediacom | 2,000Mbps |
| Optimum | 940Mbps |
| Sparklight | 2,000Mbps |
| Spectrum | 1,000Mbps |
| WOW! | 1,200Mbps |
| Xfinity | 2,000Mbps |
Find internet service in your area?
Enter your zip code below to see what internet connection types and speed tiers are available to you.
How much internet speed you need for Zoom and other video conferencing applications
| Video chat application | Minimum speed | Recommended speed |
|---|---|---|
| Zoom | 600Kbps | 3.8Mbps |
| Google Meet | 2.6Mbps | 4.0Mbps |
| Slack | 200Mbps | 2Mbps |
| Microsoft Teams | 250Mbps | 2,500Mbps |
| Video chat application | Zoom |
| Minimum speed | 600Kbps |
| Recommended speed | 3.8Mbps |
| Video chat application | Google Meet |
| Minimum speed | 2.6Mbps |
| Recommended speed | 4.0Mbps |
| Video chat application | Slack |
| Minimum speed | 200Mbps |
| Recommended speed | 2Mbps |
| Video chat application | Microsoft Teams |
| Minimum speed | 250Mbps |
| Recommended speed | 2,500Mbps |
Video calls require you to send and receive real-time video simultaneously, so there are a few internet speed factors you should keep in mind to get the most out of your remote meetings: download speed, upload speed, and latency.
Here’s more on each:
- Download speed affects how well your connection receives video from other people on the call.
- Upload speed affects how well your connection can send your video stream to others.
- Latency affects how well your connections synchronize with each other, and high latency can distort calls and cause lag.
Most video conferencing applications work best with less than 150 ms of latency. You can’t control your connection’s latency as directly as you can improve your speed by upgrading, but lower latency is better. Moreover, certain types of internet connections (like fiber) tend to have lower latency than others (like satellite internet).
Video calling apps don’t require very much speed. Most households with an internet connection can manage at least the minimum requirements. That’s great because it means we can all stay connected.
If you run into issues, your upload speed is the most likely culprit. Cable and DSL internet providers give customers much less upload speed than download. So even if your download speed is safely in the clear for video calls, your upload speed might not be up to par for big group calls. Turn off your video or switch to a wired connection for better results.
How much internet speed you need for email and chat applications
You need only about 1Mbps of download speed per instance for chat and email.
However, you may need more bandwidth when you share photos or videos in conversations and when you download larger assets (like images and attachments) from emails.
Thankfully, you can carry on with your chat and email conversations while you work on other projects without worrying about internet interruptions. That’s because the chat functions of Microsoft Teams, Facebook Messenger, Slack, and similar applications usually don’t use a lot of bandwidth.
How much internet speed you need for web browsing
We recommend about 5Mbps of download speed for heavy web browsing and jumping between sites.
Browsing the internet doesn’t take too much data unless you visit pages with a lot of uncompressed images or video content. If you’re scrolling through social media, we suggest slightly higher speeds than our general recommendation, especially if you have video autoplay enabled.
The average web page uses about 3MB (megabytes) of data. That translates to 24Mb (megabits) because there are eight bits in one byte. So if you want a whole web page to load within a second, 24Mbps of download speed would be great.
You don’t always need to load all assets on a web page to start getting to the content you want, and loading a web page doesn’t take a continuous stream of data—you just download the content once, and that’s all you need as long as you keep that web page in your browser’s cache.
How much internet speed you need for streaming
We recommend 5Mbps of download speed at a minimum per person for streaming media.
If you stream music or have a show streaming in the background while you work (or someone else in your house is binge-watching all of The Boys on Prime Video), make sure to factor that into how much bandwidth you need to work from home effectively. This is especially important for video services like YouTube or Netflix because video can be a bit of a bandwidth hog.
| Activity | Min. download speed |
|---|---|
| Streaming music on Pandora or Spotify | 1Mbps |
| Streaming music or video on YouTube | 2Mbps |
| Streaming video on Netflix, Hulu, etc. | 5Mbps |
If you want to use YouTube or a streaming service like Netflix while working from home but run into bandwidth issues like buffering, check your video quality settings. YouTube videos can run on as little as 0.7Mbps at 360p, but they can use up to 20Mbps if you’re watching in 4K.
Similarly, standard-definition Netflix can work with as little as 0.5Mbps, but Netflix in 4K uses up to 25Mbps. And if you’re using it only as background noise, you don’t need 4K.
Fortunately, most video apps can automatically detect your bandwidth availability and adjust resolution on the fly.
How much internet speed you need for sharing large files
We recommend at least 10Mbps of download and upload speeds for sharing large files.
For jobs that necessitate a large amount of file sharing, the faster your internet is, the better. That’s not to say you absolutely need fast internet speeds to download and upload large files, but it makes things go much faster and more smoothly.
Here are a few examples of how long it would take to transfer various sizes of files using common internet speeds.
| 25Mbps down/3Mbps up | 100Mbps down/10Mbps up | 1,000Mbps down/1,000Mbps up | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Downloading a hi-res image file (5 MB) | 1 second | Less than 1 second | Less than 1 second |
| Downloading a small video file (300 MB) | 1 minute, 45 seconds | 26 seconds | 2 seconds |
| Downloading a large video file (10 GB) | 1 hour | 15 minutes | 1 minute, 30 seconds |
| Uploading a hi-res image (5 MB) | 14 seconds | 4 seconds | Less than 1 second |
| Uploading a small video file (300 MB) | 14 minutes, 40 seconds | 4 minutes, 24 seconds | 2 seconds |
| Uploading a large video file (10 GB) | 8 hours, 20 minutes | 2 hours, 30 minutes | 1 minute, 30 seconds |
| Downloading a hi-res image file (5 MB) | |
| 25Mbps down/3Mbps up | 1 second |
| 100Mbps down/10Mbps up | Less than 1 second |
| 1,000Mbps down/1,000Mbps up | Less than 1 second |
| Downloading a small video file (300 MB) | |
| 25Mbps down/3Mbps up | 1 minute, 45 seconds |
| 100Mbps down/10Mbps up | 26 seconds |
| 1,000Mbps down/1,000Mbps up | 2 seconds |
| Downloading a large video file (10 GB) | |
| 25Mbps down/3Mbps up | 1 hour |
| 100Mbps down/10Mbps up | 15 minutes |
| 1,000Mbps down/1,000Mbps up | 1 minute, 30 seconds |
| Uploading a hi-res image (5 MB) | |
| 25Mbps down/3Mbps up | 14 seconds |
| 100Mbps down/10Mbps up | 4 seconds |
| 1,000Mbps down/1,000Mbps up | Less than 1 second |
| Uploading a small video file (300 MB) | |
| 25Mbps down/3Mbps up | 14 minutes, 40 seconds |
| 100Mbps down/10Mbps up | 4 minutes, 24 seconds |
| 1,000Mbps down/1,000Mbps up | 2 seconds |
| Uploading a large video file (10 GB) | |
| 25Mbps down/3Mbps up | 8 hours, 20 minutes |
| 100Mbps down/10Mbps up | 2 hours, 30 minutes |
| 1,000Mbps down/1,000Mbps up | 1 minute, 30 seconds |
What else affects how much speed you need to work from home?
Many factors play into your internet connection needs, including your job, the applications you use for work, and, most importantly, how many other people are using your home internet.
You’ll need more internet speed if, for instance, your kids, partner, or roommates are also online playing games, watching Netflix, or working from home. And you’ll want faster speeds if you handle a lot of large files and media (like uploading video) or if your job requires a VPN.
Our internet speed recommendations are generalized. You may need less or want much more. Many internet service providers offer customers speeds much higher than this recommendation—all the way up to 50,000Mbps (50Gbps).
Beyond the speeds you get from your internet provider, older home networking equipment, your network layout, and inefficient connections in your home can also affect your internet speeds. If your internet speed woes stem from something in your network rather than the speeds from your provider, check out our guide to faster internet in your home.
What to do if your internet speeds aren’t fast enough
If you’re running into problems with your internet connection and slow speeds are to blame, the first thing you should do is run a wired speed test from your modem or ONT to rule out your internet connection. If it’s slower than advertised, contact your internet provider.
If your actual internet speed isn’t an issue, connect your work device to the router using an Ethernet cable and recheck your speeds. You shouldn’t see a major difference, but if you do, you may need a replacement. We have dozens of upgrade suggestions based on routers we’ve tested and reviewed.
But if your work device’s wired connection to the router checks out, try the following to alleviate your speed woes:
- Reposition the router to a better location
- Limit nonessential internet traffic during work hours
- Get a Wi-Fi extender and place it close to your work area
- Add another satellite if you have a mesh system
- Make sure each external is vertical if your router only covers one floor
Are you maxing out speeds from your provider?
If you need more speed than you can get from the provider you already have, it’s time to find an alternative. In 2026, there are more choices than ever.
Enter your zip code to get started.
FAQ about internet speed needs for working remotely
What is a good internet speed to work from home?
What is a fast internet speed?
What is the average internet speed in the US?
Does shutting off video help meetings?
Why does my internet slow down at certain times?
Watching other people play video games is almost as popular as playing them yourself. And people aren’t just watching big-name internet celebrities either. Twitch, the most popular game streaming platform, has over four million unique creators streaming every month.1 If you like sharing your gaming experiences with the world, or even just your friends, you could become one of them.
One of the keys to a successful stream is an internet connection that can handle the video (like fiber). No one wants to spend time and money getting your lights and camera just right only for your internet connection to reduce your stream to a choppy, pixelated mess.
But not to worry! We’re here to walk you through everything you need to know about internet speeds and live video game streaming so you can get your stream just right.
Livestreaming is all about upload speed
Livestreaming is one of the few situations when download speed (the speed your internet plan typically advertises) doesn’t really matter. All you have to worry about is your upload speed. You can learn more about the difference between download and upload speed here.
Need a connection with more upload speed? See what’s available in your area.
When you’re livestreaming, video captured from your device is sent, or uploaded, from your home to video servers somewhere on the internet. This is the opposite direction that video data usually flows since most people consume more online video content than they create.
One more time: download speed doesn’t matter for livestreaming.
Upload speed is often a bit more difficult to estimate because most internet service providers (ISPs) don’t advertise it as prominently as they do download speeds (your “advertised” speed refers to your download speed). For most kinds of internet connection, your upload speed will be much lower than your download speed. Upload speed can also fluctuate, so the easiest way to find your actual upload speed is to take a speed test. If you want an upload speed that can match your download speed, your best bet is fiber.
Test and track your internet speed on your phone
Download our free, easy-to-use speed test app for quick and reliable results.
Get your upload speed
Want to find out what upload and download speed you’re currently getting? Take a speed test.
That said, there are still plenty of online activities that require a good download speed. If you’re playing a game online or streaming royalty-free music while you’re on stream, you need to make sure you have enough download speed to ensure a smooth experience. However, the only number you need to worry about for getting your stream online is your upload speed.
Upload speed requirements for livestreaming across video platforms
We recommend having a minimum upload speed of at least 10 Mbps for livestreaming. On most platforms, this will give you a slight buffer to account for fluctuations in upload speed.
Different streaming platforms have different requirements when it comes to video quality. Some are optimized so that you can broadcast low-resolution video from your cell phone whenever you want, while others try to make it possible for viewers to tune in to TV-quality streams. While you can technically stream as long as you meet the minimum requirements, you should always plan to have at least an extra 5 Mbps to account for fluctuations in speed.
Here’s the breakdown of how much upload speed you’ll need to livestream on different platforms.
Twitch
| Resolution | Min. upload speed |
|---|---|
| 720p (30 fps) | 3 Mbps |
| 720p (60 fps) | 4.5 Mbps |
| 1080p (30 fps) | 4.5 Mbps |
| 1080p (60 fps) | 6 Mbps |
Twitch is the biggest site for video game streaming, so if you want to be a streamer, you should be able to stream on Twitch. Fortunately, it gives streamers a few different recommendations for resolution and frame rate.
For context, 30 frames per second (fps) is the standard frame rate for television, while 60 fps is a common framerate in video games. Just like resolution, frame rate affects the amount of speed you need to stream, so if you don’t have the fastest connection, you might have to make a trade-off.
Facebook Live
| Resolution | Min. upload speed |
|---|---|
| 720p (30 fps) | 4 Mbps |
Facebook keeps it simple, listing only the absolute minimum requirements for streaming on the platform. But that’s not to say you can’t achieve a decent video quality with Facebook.
Although you can start a livestream on Facebook with nothing more than your phone and the Facebook app, Facebook Live is also compatible with standard streaming software like OBS Studio, Streamlabs OBS, and vMix.
YouTube Live
| Resolution | Min. upload speed |
|---|---|
| 240p | 0.3 Mbps |
| 480p | 0.4 Mbps |
| 720p (60 fps) | 2.2 Mbps |
| 1080p (60 fps) | 3 Mbps |
| 1440p (60 fps) | 9 Mbps |
| 4K/2160p (30 fps) | 13 Mbps |
| 4K/2160p (60 fps) | 20 Mbps |
YouTube has a staggering amount of recommendations, ranging from a 240p stream (which is the resolution of an old Nokia cell phone or a Game Boy Advance) to streaming in full 4K UHD.2, 3 We’d recommend shooting for somewhere in the middle. Plenty of professional streamers stream at 1080p, and that’s a high enough resolution to look good on everything from cell phones to TV screens.
You need extra internet speed for a stable video stream
We suggest that you try to have 10–15 Mbps more upload speed than the minimum requirement for the quality of video you’re trying to stream and even more if you know that your connection has regular issues with slowdown.
Another good rule of thumb is to have twice as much upload speed as whatever you set your bitrate to be, just to be safe. Not all your viewers will notice the subtle difference between 30 and 60 fps, but everyone will notice if your stream starts freezing and stuttering.
If you just barely meet the speed requirements for the video you’re trying to stream, the slightest fluctuation in your connection can interfere with or even crash your stream. That’s because livestreaming is a lot trickier than streaming video from Netflix. Since your stream isn’t prerecorded, the server can’t buffer to smooth out the normal ups and downs in internet speed.
Also, remember that if you’re streaming to multiple platforms simultaneously, you need enough total bandwidth that each stream has plenty of upload speed. For example, if you’re streaming 1080p video to both Twitch (6 Mbps minimum) and YouTube (3 Mbps minimum), you’d need an upload speed of at least 9 Mbps, though realistically, you’d need 15–20 Mbps to keep both streams stable.
Why is a stable video stream so important?
Livestreaming is much more technologically demanding than just playing games. Most online games can get by on a pretty modest internet connection, as long as there’s low latency. Livestreaming turns your home into your own personal TV station, broadcasting high-resolution video to your fans.
To grow an avid fan base on a platform like Twitch, you need to deliver a quality experience. A reliable camera, good audio equipment, and a fancy gaming computer are all important investments for any dedicated streamer, but none of that makes much of a difference to those watching if your stream freezes and staggers throughout the broadcast.
A reliable internet connection is one of the first investments an aspiring streamer should make.
What type of internet is best for livestreaming?
The best internet connection for livestreaming is fiber. To livestream, you need a reliable connection with good upload speeds and low latency. In all three of those categories, fiber-optic connections are by far the best option. If fiber isn’t available in your area, you probably want to go with a wired connection, as wireless connections tend to be more susceptible to interference and generally experience higher latency.
Fiber, is the best connection for livestreaming. It has symmetrical upload and download speeds, which means if you have gigabit download speeds, you get the exact same speeds for your uploads. Fiber is also a much more stable connection and doesn’t suffer from the same kind of slowing issues that cable has to deal with. All these factors make fiber the ideal connection for streamers.
Cable connections can reach upload speeds between 5 Mbps and 50 Mbps, so the best cable plans can handle HD streaming, but slower connections will be lucky to deliver anything above Game Boy quality. Cable is also prone to slowing down at peak hours, so unless you stream in the middle of the night, you might have to plan around the inevitable drop in speed.
DSL and satellite connections generally aren’t fast or stable enough for streamers, so you’re probably going to need either cable or fiber internet.
For more information, check out our page on fiber providers.
How does latency affect livestreaming?
Latency is the time it takes for a signal to travel from your computer to a server on the internet. It essentially determines the reaction time of your internet connection. Having high latency will cause lag in games or calls, delaying your reactions and causing problems.
Because streaming is primarily one-way communication, latency is handled a bit differently than it is in a video call. Streaming software usually performs more encoding and compression on your video (though you can adjust this in your settings) in order to improve the final quality at the expense of a few seconds of delay. This isn’t usually noticeable to your audience unless you’re streaming a Q&A session or a live event.
One important precaution for streamers to take is to use a wired connection to your router instead of Wi-Fi when possible. Even fast, reliable Wi-Fi introduces a bit of extra latency into your connection, so a wired connection is definitely preferable. If you don’t already have one, get yourself an Ethernet cable.
Why am I still getting dropped frames?
Do you have a solid internet connection but your video still looks choppy? Video game streams often suffer from dropped frames, where instead of the video playing smoothly from one frame to the next, the same frame will play twice in a row and then skip forward. If enough frames are dropped, it can lead to jittery, uneven video.
Although a slow or unstable internet connection can cause a stream to drop frames, dropped frames are often a problem with your capture card. If your capture card can’t record and encode your video data fast enough to keep up with your framerate, the result is dropped frames in your stream.
Before you fork out the money to upgrade to a better capture card, there are a few things you can try. First, check your internet speed to make sure you’re getting the upload speed you think you are. Also, make sure that you’re plugged into your router and not relying on Wi-Fi.
If you try those things and are sure that it’s not your connection, try adjusting the settings in your streaming software, lowering your bitrate. You can also try updating your computer’s network drivers.
- Twitch, “Press Center,” Accessed October 5, 2020.
- Nokia Museum, “Nokia Asha 301,” Accessed October 5, 2020.
- CNET, “Nintendo Game Boy Advance Specs,” Accessed October 5, 2020
You need only about 10Mbps of download speed to use Zoom for video conferencing, but you also need fast upload speeds, low latency, a laptop or smartphone that’s up to snuff, and a decent router or gateway.
Our guide below explains why you need more than Zoom’s recommended 1.5Mbps of download speed to have a good experience. We’ll also help you troubleshoot, shop for a great internet plan for Zoom, and offer ways to help you save on internet data during Zoom sessions.
On this page:
Download speeds for Zoom | Upload speeds for Zoom | Take a speed test | Is your internet fast enough? | Best internet providers for Zoom | Other video chat apps | Zoom troubleshooting | Data needs for Zoom | FAQs
On this page:
How much internet speed do you need for Zoom?
You need a minimum internet speed of 0.6–1.5Mbps to use Zoom, but we recommend download speeds of about 20Mbps and upload speeds of about 5Mbps for the best experience.
You also need to save speed for everything else happening on your internet connection, whether that’s a kiddo gaming in another room, a roommate on a video call of their own, or app updates on your smartphone.
If you disconnect all your other devices from Wi-Fi and close all your other apps, here’s the minimum internet speed you need for Zoom.
| Activity* | Required internet speed (upload/download) |
|---|---|
| 1:1 video call in “high-quality video” (480p)** | 600Kbps/600Kbps (0.6 Mbps) |
| 1:1 video call in 720p HD | 1.2Mbps/1.2Mbps |
| Sending and receiving video in 1080p HD | 3.8Mbps/3.0Mbps |
| Group video call in 480p SD | 1Mbps)/600Kbps |
| Group call/gallery view in 720p HD | 2.6Mbps/1.8Mbps |
| Sending and receiving group call video in 1080p HD | 3.8Mbps/3.0Mbps |
| Screen sharing with no video thumbnail | 50–75Kbps (both upload/download) |
| Screen sharing with video thumbnail | 50–150Kbps (both upload/download) |
| Audio VoiP | 60–80Kbps (both upload/download) |
| Zoom Phone | 60–100Kbps (both upload/download) |
* Data from bandwidth requirements listed on Zoom’s website.
** Zoom uses the term “high-quality video,” which doesn’t describe any industry-standard video resolution, but we interpret it to mean standard resolution of 480p.
In our Zoom testing, we experienced buffering delays, choppy video and audio, and other interruptions on Zoom calls with speeds as fast as 15Mbps. That’s why we recommend planning on at least 20Mbps of bandwidth for every video call.
The rule of thumb is that you need an internet plan with about 100Mbps of download speed per person so everyone can work, play, and stream smoothly.
Lucky for you, most internet providers offer speeds in that range. If that’s not the case for you, it might be time to switch to a faster internet provider.
Looking for faster internet speeds to combat zoom lag?
Enter your zip code below for a list of plans and providers in your area.
How much upload speed do you need for Zoom?
You need a minimum of 0.6–1Mbps of upload speed in order to use Zoom, but we usually recommend uploads speeds of about 5Mbps for the best possible experience.
Internet plans are measured primarily in download speed since we often consume most of our internet content by downloading it (think streaming video or downloading an attachment in an email). But upload speeds are also important—especially when it comes to Zooming. Watching someone else on Zoom uses download speed while sharing your own video and screen uses upload speed.
Upload speeds in most internet packages tend to be significantly slower than download speeds—in the case of cable and DSL packages, your uploads could be up to 10 times slower than your downloads. However, fiber internet often gives you matching download and upload speeds. That makes your Zoom calls go super smoothly.
Pro tip:
Want to really start vrooming when you’re Zooming? Take a look at our guide to the fastest internet providers.
Put your internet speed to the test
Take our quick speed test below to see how fast your speeds are with your current provider. Connect to your router with an Ethernet cable for the most accurate results.
Download speed
000 Mbps
Upload speed
000 Mbps
Latency (ping)
00 ms
Jitter
00 ms
Is your internet fast enough for Zoom?
Your internet is fast enough for Zoom if you have a basic Wi-Fi package on a cable or fiber connection with at least 1.5 Mbps download speeds. You also likely have fast enough speeds if you’re on a DSL or satellite plan, though you may experience slower upload speeds than what would be ideal for a totally smooth Zoom session.
If you compare Zoom’s speed requirements to the speeds you usually get from an internet provider or cellular company, it’s clear that Zoom’s bandwidth requirements are pretty easy to hit.
| Internet connection type | Typical download speed | See more |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber | 100–50,000Mbps | View Providers |
| Cable | 25–2,000Mbps | View Providers |
| DSL | 0.5–115Mbps | View Providers |
| 5G | 40–1,000Mbps | View Providers |
| 4G LTE | 5–50Mbps | View Providers |
| Fixed wireless | 5–1,000Mbps | View Providers |
| Satellite | 12–400Mbps | View Providers |
It won’t be hard to hit Zoom’s basic internet speed requirements with a cable, fiber, or DSL plan.
Nowadays, you can even get solid speeds for using Zoom over a satellite internet connection. But since it involves streaming video, Zoom consumes a great deal of internet data—so you’ll want to be sure to get a satellite internet plan that doesn’t have strict data caps or a lot of lag.
Internet providers with the best Zoom speeds
| Provider | Starting price | Top download speed | Top upload speed | Order online |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| $40/mo.* for 12 mos. | 2,000Mbps | 250Mbps | View Plans for Xfinity |
|
| $40/mo.† | 400Mbps | 40Mbps | View Plans for Starlink |
|
| $70/mo.‡ | 8,000Mbps | 8,000Mbps | View Plans for Google Fiber |
|
| $39.95/mo.§ | 5,000Mbps | 5,000Mbps | View Plans for EarthLink |
|
| $30/mo.║ | 5,000Mbps | 1,000Mbps | View Plans for Astound |
| $34/mo.** | 5,000Mbps | 5,000Mpbs |
See disclaimers.
Many internet providers can get you Zoom’s minimum speeds, but we wanted to highlight some of our favorites. Xfinity is probably your best bet because it has a wide network, incredibly fast speeds, and great customer ratings.
But fiber providers such as Google Fiber and AT&T give you the added advantage of having very fast upload speeds, ensuring your video feed stays strong.
T-Mobile 5G home internet also did well on our Zoom tests, and we love that it’s available almost anywhere you can get a strong 5G signal on your phone.
You can find more great providers on our fastest internet providers guide. Also, make sure to run a search to see which of these providers are available in your area.
Ready to start shopping for a new internet provider?
Enter your zip code to get a list of all internet options near you.
Speed requirements for other videoconferencing apps
| App | Min. speed requirement for video calls (download/upload) |
|---|---|
| Skype | 512Kbps/128Kbps |
| Slack | 600Kbps/600Kbps |
| Cisco Webex | 500Kbps/500Kbps |
| Google Meet | 1 Mbps/1Mbps |
| Microsoft Teams | 1.5Mbps/2Mbps |
Data from Skype, Slack, Cisco Webex, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams speed requirements pages.
You need a minimum of at least 500Kbps (0.5 Mbps) to make video calls on videoconferencing apps other than Zoom.
The internet speed requirements on apps like Skype, Slack, and Google Meet are pretty much the same as Zoom’s requirements. You don’t need a lot of bandwidth to make the apps work, but a faster internet speed reduces the chance of frustrations like poor connections or dropped calls.
How to troubleshoot your Zoom connection
If your Zoom sessions frequently lag or freeze up, it might be an internet connection that’s too slow. But it could also be a problem with your laptop, your router, or Zoom itself.
Follow the steps below to get back up and zooming in no time.
Step 1: See if Zoom itself is the problem
Sometime’s the problem isn’t you—it’s Zoom itself. Head over to the Zoom Status checker to see if the service is reporting any widespread problems.
Step 2: Update your Zoom app
We recommend downloading and using the Zoom app on your laptop rather than trying to join meetings from your browser or smartphone. If you’re on the app but still having trouble, make sure you’re using the latest version and have installed all the updates.
Step 3: Close other applications
If you’re on a slow internet connection, multitasking can slow down your Zoom connection. To bring your Zoom call back to normal, close out your email, web browser, and any other applications or windows you might have open.
Step 4: Restart your modem and router
The quickest and easiest way to address slow internet at home is by restarting your modem and router. Unplug both devices from the wall, let them rest for a minute or so, and then plug them back in. A simple reset clears potential bugs and programming cobwebs that may be weighing down your equipment.
Step 5: Use mobile data or a hotspot
Has your home internet cut out? Simply whip out your cell phone and log on to Zoom with your mobile data. Most cell phones also have a built-in hotspot feature, so if your cellular plan allows it, you can switch on your phone’s hotspot to create Wi-Fi access for your laptop or desktop computer.
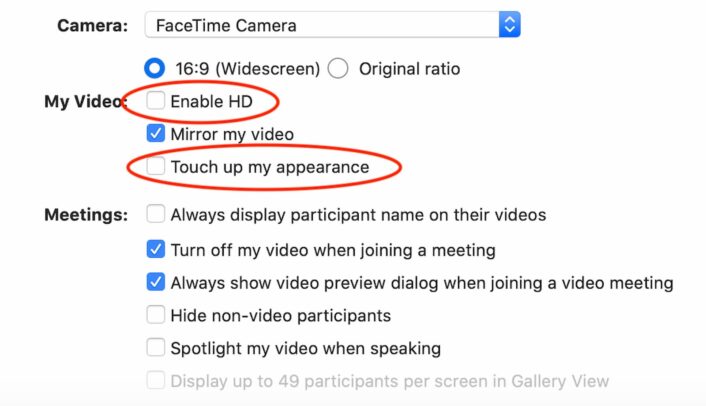
Step 6: Switch off “Enable HD” and “Touch up my appearance”
Zoom’s “Enable HD” and “Touch up my appearance” features both take extra bandwidth and data to function, so you can get better performance by switching them off.
To turn them off, head to the video settings menu by clicking the tiny, upward-pointing arrow next to the Start Video button in the bottom left corner of your screen. There you can click off the check marks on both features.
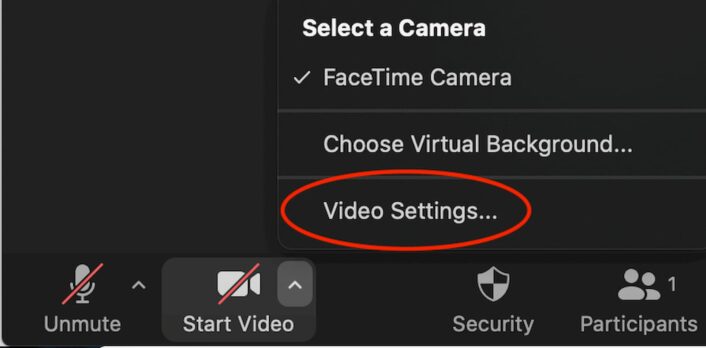
Step 7: Turn off the Wi-Fi on other devices
The more people using your Wi-Fi connection, the more strain it puts on your home internet speed. If your kids or roommates are streaming video or playing games on their devices while you’re in a Zoom meeting, ask them to switch it off so you can get a better connection. If asking nicely doesn’t work, you can kick them off by logging into your router.
Pro tip:
Read our guide to internet speed and working from home to get an idea of how much bandwidth you need when you’re teleconferencing and studying in the house.
Step 8: Move your device closer to your router (or move your router to a better place in your house)
You may be in a part of the house with a Wi-Fi dead zone, where the router’s signal can’t reach your device. If that’s the case, take a seat on a couch or a chair within eyeshot of your router to improve the signal.
To improve the Wi-Fi signal, you could also move your router so it’s in a more centralized position in your house. Place it on a table or shelf, away from metal objects, microwaves, and other obstacles. If your home has multiple floors or a complex layout, consider investing in a mesh wireless system or long-range router.
Step 9: Connect to your router with an Ethernet cable
Instead of relying on a Wi-Fi signal, you can plug your computer directly into your router with an Ethernet cable. That gives you faster speeds and more reliable performance.
Step 10: Upgrade your internet plan—or switch providers
If you’re still having trouble, consider calling your internet provider to upgrade your internet speed. Or, if other options are available in your area, you can switch to a new provider that gives you faster speeds and better performance overall.
Still not getting the speeds you need for Zoom?
Search for a new internet provider in your area by entering your zip code below.
Pro tip:
Is your internet down? Take a gander at our guide to troubleshooting internet to get your Wi-Fi back up and running.
How much data do you need to use Zoom?
| Activity | Amount of data used |
|---|---|
| 1:1 call in “high-quality video” (480p)* | 540MB/hr. |
| 1:1 video call (720p) | 1.08GB/hr. |
| 1:1 video call (1080p) | 1.62GB/hr. |
| Group call in “high-quality video” (480p)* | 810MB/hr. |
| Group video call (720p) | 1.35GB/hr. |
| Group video call (1080p) | 2.475GB/hr. |
| Audio-only VoIP | 27–36MB/hr. |
| Screen sharing | 22.5MB/hr. |
| Screen sharing (with thumbnail) | 67.5MB/hr. |
| Activity | 1:1 call in “high-quality video” (480p)* |
| Amount of data used | 540MB/hr. |
| Activity | 1:1 video call (720p) |
| Amount of data used | 1.08GB/hr. |
| Activity | 1:1 video call (1080p) |
| Amount of data used | 1.62GB/hr. |
| Activity | Group call in “high-quality video” (480p)* |
| Amount of data used | 810MB/hr. |
| Activity | Group video call (720p) |
| Amount of data used | 1.35GB/hr. |
| Activity | Group video call (1080p) |
| Amount of data used | 2.475GB/hr. |
| Activity | Audio-only VoIP |
| Amount of data used | 27–36MB/hr. |
| Activity | Screen sharing |
| Amount of data used | 22.5MB/hr. |
| Activity | Screen sharing (with thumbnail) |
| Amount of data used | 67.5MB/hr. |
* Zoom uses the term “high-quality video,” which doesn’t describe any industry-standard video resolution, but we interpret it to mean standard resolution of 480p.
Even though using Zoom doesn’t require fast speeds, it can use quite a bit of data. Drawing from our knowledge of the difference between megabits and megabytes, we did some calculations to get a baseline estimate. We found that you can end up using anywhere from 0.5GB to a whopping 2.5GB per hour on a Zoom call with video enabled.
Pro tip:
Worried about Zooming away your monthly data cap? Read our data caps guide to find internet providers with no caps.
The chart below gives you an idea of some other popular tasks and how much data they devour. Zoom doesn’t appear to need as much as streaming services like Netflix—but keep in mind that your Zoom data usage could vary depending on your connection and your device.
| Activity | Data used* |
|---|---|
| Streaming video in SD | 500MB/hr. |
| Streaming video in HD | 2GB/hr. |
| Streaming video in 4K | 8GB/hr. |
| Gaming on Xbox Live or PS4 | 200MB/hr. |
| Streaming music | 60MB/hr. |
| Checking email | 10MB per 25 emails |
| Downloading a 1 GB file | 1GB |
| Activity | Streaming video in SD |
| Data used* | 500MB/hr. |
| Activity | Streaming video in HD |
| Data used* | 2GB/hr. |
| Activity | Streaming video in 4K |
| Data used* | 8GB/hr. |
| Activity | Gaming on Xbox Live or PS4 |
| Data used* | 200MB/hr. |
| Activity | Streaming music |
| Data used* | 60MB/hr. |
| Activity | Checking email |
| Data used* | 10MB per 25 emails |
| Activity | Downloading a 1 GB file |
| Data used* | 1GB |
* Estimates based on Armstrong’s data usage calculator.
How do you use less data on Zoom?
The best way to use less internet data while on a Zoom call is to switch off your video.
If you have strict data restrictions on your internet or mobile plan, you can save data by using Zoom as an audio-only VoIP service. By our calculations, voice calls eat up only around 31.5MB of data per hour—a fraction of how much you would use when your video is switched on. Screen sharing with no video uses 22.5–67.5MB per hour.
Of course, you won’t have to worry about that if you have unlimited data on your internet or mobile plan.
Zoom FAQs
How do you turn off HD video on Zoom?
Do Zoom's AI tools require faster speeds or extra data?
Is 5G home internet fast enough for Zoom?
Is 25 Mbps fast enough for Zoom?
How much bandwidth does Zoom use?
How much data does Zoom use?
Does Zoom work without Wi-Fi?
Disclaimers
* Xfinity
For 12 months, no term contract. Restrictions apply. Autopay w/ stored bank account and paperless billing req’d. Taxes and fees extra and subj. to change. Reduced speeds after 30 GB of usage/line. Data thresholds may vary.
† Starlink
Plus hardware, shipping & handling fees, and tax. Fully refundable. Depending on location, some orders may take 2 weeks or more to fulfill.
‡ Google Fiber
Plus taxes and fees. Upload/download speed and device streaming claims are based on maximum wired speeds. Actual Internet speeds are not guaranteed and may vary based on factors such as hardware and software limitations, latency, packet loss, etc.
§ EarthLink
with a 12 month contract. Actual speeds may vary depending on the distance, line-quality, phone service provider, and number of devices used concurrently. All speeds not available in all areas
║ Astound
Observed speeds may vary | One-time fees extra | Restrictions apply | Not available in all areas | New residential customers only
** AT&T
Price includes $10/mo. discount when you sign up for paperless billing and AutoPay with a debit card or bank account. Or $5/mo. with a credit card.

Nearly every internet service provider (ISP) offers multiple plans, each offering different download and upload speeds. If you’re in the market for a new internet service, which one should you pick? Do you always pick the fastest you can afford?
Residential internet speeds have increased rapidly over the last few years, so for many people, top-tier internet plans offer more speed than they could possibly use. But what’s a good download and upload speed for you? You don’t want to pay for a plan that’s faster than what you need, so we’ll break down the details so you can pick the plan that’s right for you.
What is a good download speed?
A good rule of thumb for how much internet download speed you need is 10Mbps per person. Of course, what a good download speed is for you heavily depends on what you do online and how many devices are on your home network. For basic web surfing or email, 10Mbps is enough to give you a seamless online experience.
Video streaming services like Netflix and Hulu, on the other hand, are some of the most bandwidth-intensive activities that people engage in. If you have several TVs in your house all streaming movies along with iPads streaming YouTube, you’re going to want a download speed that can do some heavy lifting to avoid constant buffering.
Not sure what speed your devices need to keep functioning smoothly?
You can use our How Much Speed Do I Need? Tool. It’ll help you know exactly how much download speed you need to have a seamless internet experience at home.
How Much Internet Speed Do You Need?
Est. Time: 60 seconds
Answer 6 questions and get a personalized internet speed recommendation!
How many people in your household use the internet/WiFi on a daily basis?
How many devices in your home connect to the internet, including tablets, gaming consoles, and smart devices?
How many people in your household work from home?
What video quality do you use for streaming TV and movies?
How intensely does your household participate in online gaming?
Does your household download large files from the cloud or via the internet?
What is a good upload speed?
For the average internet user, a good upload speed to shoot for is 5Mbps. Asymmetric DSL (ADSL) usually has speeds up to 1.5Mbps, while cable internet can have upload speeds from 5Mbps to 50Mbps.
For basic online activities like surfing the web and checking email, even ADSL’s 1.5Mbps is more than enough for a smooth internet experience. Upload speed becomes much more important if you want to use video chat, upload high-resolution images, or livestream video from your home.
If you use your home network for work, school, or watching video on a regular basis, ADSL’s low upload speeds are definitely going to be a problem. At the very minimum, you’re going to want to find a cable provider that has upload speeds on the high end, between 25Mbps and 50Mbps.
An even better solution for those who rely on uploading is fiber. Fiber-optic networks have symmetrical upload speeds, which means if you have a 1Gbps (1,000Mbps) connection, you have 1Gbps upload and 1Gbps download speeds. Fiber is also the most reliable type of connection, making your online experience much less likely to have issues—even if you stream at peak-use times. If you livestream on platforms like Twitch or YouTube, a fiber connection is a must.
While it’s tempting to dismiss upload bandwidth as something needed only by businesses and content creators, it’s worth noting that upload traffic increased dramatically after the COVID-19 outbreak as people had to figure out new ways to live their lives at a distance.1 For many households trying to keep up with work, school, and social connections, upload speed suddenly became the bottleneck.
New internet providers have arrived
The internet is changing quickly with new technologies like 5G home internet and high-speed satellite broadband. There’s a good chance you have access to some new ISPs—enter your zip code to find out.
What is a good Wi-Fi speed?
Many Wi-Fi routers boast incredibly high speeds due to having dual-band or tri-band technology, which essentially allows them to broadcast multiple Wi-Fi networks at the same time. This can be really important if you have a lot of devices on your home network. Multiple signal bands, along with other features like beamforming, MU-MIMO (multi-user, multiple input, multiple output), and other Wi-Fi 6 (and now Wi-Fi 7) technologies, can allow your devices to take maximum advantage of your high-speed internet connection.
For more information on how to get the most out of your Wi-Fi network, check out our look at the fastest gigabit routers and the fastest gigabit modems currently on the market.
What’s a good speed for my connection type?
| Connection type | Advertised download speeds | Advertised upload speeds |
|---|---|---|
| DSL | 3–145Mbps | 1–20Mbps |
| Cable | 25–1,000Mbps | 1–50Mbps |
| Fixed wireless | 25–300Mbps | 1–50Mbps |
| 4G LTE home | 9–60Mbps | 1–30Mbps |
| Fiber | 30–5,000Mbps | 30–5,000Mbps |
| Satellite | 12–350Mbps | 3Mbps |
Based on advertised speeds. Data as of 6/29/2023.
Providers offer different speeds at different price points, but these speeds also depend upon the constraints of the internet technology they’re using. For example, if you regularly make YouTube videos and want to upgrade your internet so you don’t have to wait so long when uploading them, you’re not going to be able to cut down your wait times by much with your current provider if they only offer DSL. On the other hand, even the slowest fiber plans offer higher upload speeds than DSL, so you might even be able to save money on your monthly bill by switching.
It’s important to note that speed isn’t the only thing that you’re paying for with an internet plan. Some plans charge more for higher monthly data caps, while others charge extra to avoid long-term contracts. Speed is an important factor in choosing an internet plan, but it’s not the only one.
What is download speed?
Download speeds determine how fast information can travel from the internet to your home. Whether you’re pulling up a website, watching Netflix, or updating your OS, all that information is coming from a server somewhere and traveling across your connection into your house. For most every activity you do on the internet, download speed is going to be the most important factor.
Download speed is also referred to as bandwidth, or the amount of data transmitted over a connection over a certain amount of time. You can think of downloading data like filling a swimming pool with a hose. A bigger hose allows more water to flow through it, and the pool fills more quickly. Likewise, a connection with more bandwidth will download files much more quickly.
Most of the time when people talk about internet speed, they’re talking about download speed or bandwidth. This is also the speed that providers generally refer to with their advertised speeds.
Pro Tip:
Faster download speeds are great, but faster speeds mean more data traveling through your connection. Be aware if your provider has data caps, as a faster connection means you will hit those limits sooner.
What is upload speed?
Upload speeds are used when you want to send information from your device to another location on the internet. Although we don’t think about it as much as we think about downloading information, we upload information all the time. We use our upload speed when we want to post a video to Facebook, or send a picture from our phone to a friend. We also use it every time we click on a link or type a search term into Google. That information has to travel from our browser to the appropriate server in order to tell it which information it needs to send us. Uploading is an essential part of using the internet.
We all use upload speed, but some people rely on it heavily. If you’re a content creator that works with video, audio, or other media with large file sizes, slow upload speeds could mean waiting for hours to post your content online or store it on a cloud-based server. If you livestream video or use video chat like Zoom or Skype, you won’t even be able to connect if your bandwidth is too low.
Most ISPs advertise only download speeds, so you might not even realize that upload speeds are a separate thing. Download speeds are also generally the faster of the two speeds, so most advertisements tend to focus on them.
Download speed is generally more important than upload speed
Although we constantly both download and upload information online, for most of us, the information we upload is generally much smaller. If you’re looking for a new hat on Amazon, for example, your browser is constantly downloading images and text as you browse, as well as downloading the advertisements that pop up alongside your search results. By contrast, the only information that needs to be uploaded are the search terms you look up and the information from the links and buttons you click. This is why upload speeds usually don’t need to be as fast as download speeds.
How do I know if I need more speed?
The surest sign that your internet speed isn’t meeting your needs is when you face long loading times, unexpected pauses, and crashed programs when using the internet. Most of us have had to deal with slow download speeds at one point or another, which often involves waiting for images to appear on a web page or a video stopping in the middle of playback to buffer.
If you don’t have enough upload speed, you might get an unusually long wait time when uploading a video to Facebook or you might have your call dropped when trying to use video chat. Since many types of internet connection heavily favor download speeds, it often doesn’t take much to overwhelm your upload bandwidth.
Just because you experience a slowdown in your connection doesn’t necessarily mean it’s time to upgrade your internet service. There are several reasons why your internet speed might dip temporarily due to traffic or routine maintenance. There are also a few steps you can take to troubleshoot a slow connection. But if these delays are a common occurrence that’s starting to interfere with your life, it might be worth it to switch to a faster, more reliable connection.
Bottom line: Pay only for speed you’re going to use
Fast internet is great, but paying for a faster connection than you can actually use won’t make any difference in your online experience. Choose an internet provider that meets your maximum speed requirements to avoid paying for bandwidth that you’re not going to use.
Thinking of switching to a faster plan? Enter your zip code to see which providers are available in your area.
What Is a Good Download and Upload Speed FAQ
How can I increase my download speed?
Source
- Doug Dawson, CircleID, “The Upload Crisis” May 13, 2020. Accessed June 16 2021.
Netflix is pretty amazing, but there’s a big catch. You need internet speeds of at least 25Mbps to watch in high definition.
Our expert advice is a little different from the Netflix recommendation of 3Mbps for a single show, but let us explain. In the real world, most people watch Netflix while doing 10 other internet things simultaneously on their computers, phones, or tablets. And don’t forget all those smart devices and your kids or roommates watching in the next room!
To avoid the buffer gremlins for a single Netflix stream, get internet of 25Mbps or more. You’re even better off with 100Mbps if you want to watch on multiple screens at the same time. To enjoy video streaming in 4K resolution, consider upgrading to a plan with speeds of at least 200Mbps.
Does your Wi-Fi have what it takes?
Take our speed test to see if your internet is fast enough to support your Netflix habit.
Download speed
000 Mbps
Upload speed
000 Mbps
Latency (ping)
00 ms
Jitter
00 ms
Netflix speed basics
Before we jump into the nitty-gritty, here’s a quick breakdown of three things you need to know about Netflix and internet speeds.
Three golden rules for Netflix internet:
- The more users and devices logged in at once, the more internet speed you need.
- For 4K streaming, fiber or cable internet plans are best.
- For slow connections and hotspots, choose a Netflix Basic plan.
Here are your minimum speed needs for Netflix
Netflix claims on its website that you can stream with speeds as low as 3Mbps. But that’s only if Netflix is the only app you’re using while you’re online—not an accurate reflection of how most folks spend their time on the web these days.
The experts at HighSpeedInternet.com put together some realistic Netflix speed recommendations. You can easily get these speeds on pretty much any fiber, cable, 5G plan —or even some DSL and satellite internet plans.
| Netflix Plan | Minimum required speed* | Minimum recommended speed for optimal streaming | Sign up online |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard with ads | 3Mbps | 25Mbps | Sign Up |
| Standard | 5Mbps | 100Mbps | Sign Up |
| Premium | 15Mbps | 200Mbps | Sign Up |
Recommendations from Netflix’s speed requirements page.
How Much Internet Speed Do You Need?
Est. Time: 60 seconds
Answer 6 questions and get a personalized internet speed recommendation!
How many people in your household use the internet/WiFi on a daily basis?
How many devices in your home connect to the internet, including tablets, gaming consoles, and smart devices?
How many people in your household work from home?
What video quality do you use for streaming TV and movies?
How intensely does your household participate in online gaming?
Does your household download large files from the cloud or via the internet?
Our experts say: Internet speed needs are the same for all video streaming apps
If you have enough internet speed to stream Netflix, that means you’ll have enough speed to switch over to other platforms such as Paramount+, Max, Apple TV, or YouTube TV. The only time you’ll need faster speeds is if you’re trying to stream on multiple screens at the same time.
What do you need to stream Ultra HD 4K movies on Netflix?
Many households need speeds of 200Mbps or faster to facilitate watching movies in Ultra HD 4K resolution on Netflix.
4K resolution gives you images in awe-inspiring detail, enhancing your experience for the sweeping cinematic grit of All Quiet on the Western Front or the lush splendor of a nature docuseries like Our Great National Parks. Nothing beats it, especially when you have a big screen.
The problem? 4K uses up a lot of broadband speed. Like, A LOT. Streaming in 4K also puts a massive dent in your monthly data allotment.
Here’s a breakdown of the scary stats:
- 4K requires speeds of at least 15Mbps minimum speeds for a single user to stream Netflix smoothly—3X faster than what you need to stream video in Full HD 1080p resolution.
- Watching a two-hour film in 4K consumes a whopping 16GB per hour—4X the data you would use streaming the same film HD.
Get fiber internet or a gigabit cable plan for the best 4K performance
You basically need supercharged internet to keep a 4K stream flowing without it getting bogged down by the spinning wheel of death. But you can bulk up your broadband speed with a fiber internet plan. Fiber gives you the fastest and most reliable type of internet connection, and even baseline plans get you super-smooth speeds.
If fiber internet hasn’t yet come to town, there’s a good chance you can get fast speeds from a cable internet provider. If you’re an ultra-high-def enthusiast, look for plans of about 1,000Mbps (1Gbps).
Best internet plans for 4K video streaming
| Plan | Price | Speed | Order online |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT&T Internet 300 | $55.00/mo.* | 300Mbps | |
| Verizon Fios 500 Mbps | $74.99/mo.† w/ Auto Pay | 500Mbps | View Plan |
| Google Fiber Core 1 Gig | $70.00/mo.‡ | 1,000Mbps | View Plan |
| Xfinity 1 Gig | $100.00/mo.§ for 12 mos. | 1,000Mbps | View Plan |
Read disclaimers.
Find fast internet for smooth streaming
Need a killer Wi-Fi plan to binge Better Call Saul? Run a search with your zip code to see which internet plans are available in your area.
What if you have slow internet? Never fear—you can still watch Netflix
You can pay a pretty penny for Netflix Premium and ultra-fast internet to go with it. Butdoes that mean the party is over for Netflix when you’re on a budget? Of course not.
If you’re on a budget, start by finding a budget internet plan (you’ll find some of our faves below). Then, pick a Netflix plan that doesn’t bust your wallet in half—we recommend Netflix Basic for its manageable 720p resolution.
If you want, you can lower your resolution even more. That’s something you may need to do if you’re streaming video over a hotspot. As convenient as mobile hotspots are, they come with strict internet data limits that can put a serious damper on your Netflix usage if you’re not careful. Watch a few too many movies in HD or 4K and you can use up $90 worth of data in a day.
Best internet plans for budget Netflix users
| Plan | Price | Speed | Order online |
|---|---|---|---|
| Astound 300Mbps Internet | $20.00/mo.* | 300Mbps | View Plans |
| Xfinity 500 Mbps | $55/mo.† for 12 mos. | 500Mbps | View Plans |
| T-Mobile Rely Internet | $50/mo.‡ w/ AutoPay, plus taxes & fees. | 133–415Mbps | View Plans |
| Verizon 5G Home | $50/mo.§ w/ AutoPay | Up to 300Mbps | View Plans |
Read disclaimers.
‡ Guarantee exclusions like taxes and fees apply.
§ Price per month with Auto Pay & without select 5G mobile plans. Consumer data usage is subject to the usage restrictions set forth in Verizon’s terms of service; visit: https://www.verizon.com/support/customer-agreement/ for more information about 5G Home and LTE Home Internet or https://www.verizon.com/about/terms-conditions/verizon-customer-agreement for Fios internet.
Can you stream Netflix with satellite internet?
Yes, you can definitely stream Netflix with satellite internet. But satellite has very slow speeds and (often) extremely limited data caps, so you’ll want to reduce your video resolution to the lowest-possible setting to get the most out of your Netflix experience. The image quality isn’t as nice, but low resolution keeps you from burning through a month’s worth of data in a matter of hours.
Pro tip—Get more streaming plan recommendations
Take a look at our guide to the best internet for streaming for a breakdown of top Wi-Fi plans to meet your Netflixing needs.
Here’s how to adjust the video resolution on your Netflix app
Netflix automatically chooses a video resolution based on your Netflix plan and connection speed. But you can change it manually ff your Netflix streaming falls prey to buffering and slow load times a bit too often. Lowering your video resolution will also help you reduce data usage, which is crucial if you’re worried about your data cap.
To reduce data usage and buffering, set the resolution to Medium or Low. Here’s how to do it:
On desktop:
Step 1: Sign in from your browser.
Step 2: Click your profile on the Who’s Watching? screen.
Step 3: Click Account in the drop-down menu that appears when you move your cursor over the Profile section in the top right-hand part of the screen.
Step 4: Select the profile you want to edit in Profile & Parental Controls.
Step 5: Go to Playback settings and click Change.
Step 6: Choose between Auto, Low, Medium, or High in the section titled Data usage per screen.
On mobile:
Step 1: Sign in from your browser app.
Step 2: Tap Menu on the upper left.
Step 3: Tap Account.
Step 4: Tap the profile you want to edit in Profile & Parental Controls.
Step 5: Tap Change in Playback settings.
Step 6: Choose between Auto, Low, Medium, or High in the section titled Data usage per screen, then tap Save.
Choose the best Netflix plan in an age of post-password sharing
As Netflix cracks down on password sharing—forcing customers to pay an extra $7.99 a month for any users outside a subscriber’s household—it’s important to decide which plan is best for you.
The Standard and Premium plans are best for most people because they offer higher resolution and give you more flexibility in the number of shows you can stream simultaneously.
If you have slow internet—through a DSL or satellite connection, for example—you should consider going a cheaper route with the Standard or Standard with Ads plans.
Netflix plan options
| Plan | Price | # of simultaneous streams | # of devices you can download shows on | Max video resolution | Sign up online |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard with ads | $7.99/mo. | 0 | 1 | Full HD (1080p) | Sign Up |
| Standard | $17.99/mo. | 2 | 2 | Full HD (1080p) | Sign Up |
| Premium | $24.99/mo. | 6 | 6 | Ultra HD (4K) and HDR | Sign Up |
| Standard w/extra member slots | $24.98/mo.* | 2 + 1 | 2 + 1 | Full HD (1080p) | Sign Up |
| Premium w/extra member slots | $33.98/mo.† | 6 + 2 | 6 + 2 | Ultra HD (4K) and HDR | Sign Up |
FAQ
What upload speed is good for Netflix?
Disclaimers
Best internet plans for 4K Netflix streaming (return to table)
Data effective 07/07/2025. Offers and availability may vary by location and are subject to change.
*Price after $5/mo Autopay & Paperless bill discount (w/in 2 bills). Plus taxes & fees. Monthly State Cost Recovery Charge in TX, OH, NV applies. One time install chrg may apply. Ltd. avail/areas.
‡Plus taxes and fees. Upload/download speed and device streaming claims are based on maximum wired speeds. Actual Internet speeds are not guaranteed and may vary based on factors such as hardware and software limitations, latency, packet loss, etc.
† Consumer data usage is subject to the usage restrictions set forth in Verizon’s terms of service; visit: https://www.verizon.com/support/customer-agreement/ for more information about 5G Home and LTE Home Internet or https://www.verizon.com/about/terms-conditions/verizon-customer-agreement for Fios internet.
§ For 12 months, no term contract. Restrictions apply. Autopay w/ stored bank account and paperless billing req’d. Taxes and fees extra and subj. to change. Reduced speeds after 30 GB of usage/line. Data thresholds may vary.
Best internet plans for budget Netflix users (return to table)
Data effective 07/07/2025. Offers and availability may vary by location and are subject to change.
*24 Month Internet Pricing. No contract required. Equipment priced separately. Includes $5 discount for 12 months w/ ebill & autopay. Experienced speeds may vary. New residential customers only.
† For 12 months, no term contract. Restrictions apply. Autopay w/ stored bank account and paperless billing req’d. Taxes and fees extra and subj. to change. Reduced speeds after 30 GB of usage/line. Data thresholds may vary.
‡ Guarantee exclusions like taxes and fees apply.
§ Consumer data usage is subject to the usage restrictions set forth in Verizon’s terms of service; visit: https://www.verizon.com/support/customer-agreement/ for more information about 5G Home and LTE Home Internet or https://www.verizon.com/about/terms-conditions/verizon-customer-agreement for Fios internet.
Use the tool below to check your internet speed and get results in seconds. You’ll learn upload and download speeds in megabits per second (Mbps) and latency and jitter in milliseconds (ms) based on your device, your local network, and your connection to the internet.
That’s it! You have the raw numbers, but there’s a little more to it. We’ll walk you through what it all means so you can decide whether it’s time to make a change.
What an internet speed test measures

What are Mbps?
Internet speed is measured in bits per second, and megabits stands for one million bits. Speeds are usually measured in Mbps, but sometimes measured in gigabits per second (Gbps), which is a billion bits per second.
What is download speed?
Download speed measures how fast information from the internet gets to your device (for example, how fast your Netflix show loads) in Mbps. Think of it like the time it takes a car to get from the store to your home.
How much download speed do you need?
Speeds of 100Mbps are fast enough for most online activities, and 1,000Mbps is fast enough to support multiple devices connecting at the same time. Higher is better.
What is upload speed?
Upload speed refers to how fast information on your device can be sent to some other destination on the internet (like how fast your vacation pictures post to Instagram) in Mbps. Think of it like the time it takes for a car to get from your home to the store.
How much upload speed do you need?
Upload speeds of about 20Mbps are fast enough for almost every online activity, but you may need more if you’re live-streaming from multiple devices at once. Higher is better.
What is ms?
This one’s easy! It’s the standard tech abbreviation for milliseconds, or thousands of a second. No analogy required.
What is latency?
Latency, or lag, refers to the time it takes for a signal to be sent to and from your computer to a remote server somewhere. Think of it like the round-trip travel time of a single car.
How much latency do you need?
Latency under about 30ms is adequate for most tasks, but you may need latency under 20ms for first-person shooters and racing games. Lower is better.
What is jitter?
Jitter refers to the consistency of your latency over time. If latency is the round-trip travel time of a single car, jitter measures the difference in arrival times of separate cars.
How much jitter do you need?
A decent jitter is 50ms or less, but you want around 30ms for gaming and video conferencing. Lower is better.
What is bandwidth?
Bandwidth refers to the width of the metaphorical pipe through which you’re downloading and uploading data, and it relates to your local area network rather than speeds on a single device. When you’re shopping for home internet plans, max download and upload speeds refer to your connection’s total bandwidth at any given time.
How much bandwidth do you need?
We recommend about 100Mbps of bandwidth for every person in your home using the internet at the same time. Small families can get away with 250Mbps speeds, but larger families who do a lot of gaming or remote work may be happier with plans in the 500Mbps range.
What determines your internet speed?
Your internet speed is determined by your device, your local connection, and your internet provider. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Your device: Your laptop, smartphone, desktop, or smart TV is the first link in the chain. Newer and higher-quality devices process data faster.
Your local connection: Whether you’re connected through Wi-Fi or an Ethernet cable, your local network is the next link. Like with personal devices, newer and higher-quality Wi-Fi routers and Ethernet cables translate to faster speeds.
Your internet provider: Your internet provider connects your local area network to outside networks, but is limited by both the internet plan you choose and your connection type. Generally speaking, faster connections cost more.
How internet type determines your speed

Dial-up internet is the slowest kind of internet connection and is too slow for uses like streaming video, with average speeds of 50Kbps or so (0.5Mbps). It’s mostly a relic of the past.
Satellite internet connects your local network to satellites in space, and its speeds and latency are highly variable. It’s also expensive, but you can get it almost anywhere.
Digital subscriber line (DSL) internet uses aging telephone networks and achieves speeds up to 100Mbps. It’s not much faster than satellite, and its speed and latency are affected by the distance to your internet provider’s central office.
4G LTE and 5G fixed wireless internet uses excess capacity on cell towers to provide internet to your home. Speeds can vary depending on traffic congestion and your distance from the nearest tower, but speeds can be as fast as 1,000Mbps in ideal circumstances.
Cable internet uses fiber-optics on the street and coaxial cables to connect to your home, just like cable TV. You can get download speeds up to 2Gbps, but you’ll have much slower upload speeds and may have congestion during peak hours.
Fiber internet connects you to the web via fiber-optic cables. You can get residential speeds up to 10Gbps, and you have the benefit of symmetrical upload speeds. Fiber also excels in reliability, latency, and jitter.
By understanding what kind of internet connection you have, you should have a good idea of how fast your connection should be. The question, though, is how much speed you’re actually getting from your connection.
Disappointed in your speed test results?
Enter your zip code to shop faster internet options in your neighborhood.
Tips to get the most accurate speed
You know how to see the speed you’re getting on a single device at a given moment in time, but you need a little more info to determine whether you’re getting the bandwidth you deserve from your internet provider.
Here are a few things you can do to get the most accurate results:
Pause automatic downloads
Downloads can take up a lot of your bandwidth, and that means slow speeds on a speed test. You can check the Task Manager on Windows or the Activity Monitor on macOS to see if any programs are trying to download updates or other large files.
Get rid of freeloaders
Next, make sure that no one else on your home network is using a chunk of your bandwidth. You’re not going to get very accurate results if you have people streaming Netflix in three different rooms of your house while you test. You can ask them nicely to pause their activities while you test, or go scorched earth and kick them off by logging into your router interface or changing your Wi-Fi password.
Check for wireless router issues
As mentioned above, plugging directly into your router via Ethernet will give you the fastest possible speeds. It’s impractical, though, and may not be super helpful.
We suggest you check your internet speed where you most often use your computer, on Wi-Fi. If the speed is less than you expect, try plugging it into your router. If you get a dramatic increase in speed, it might be time to get a better router.
So, what do my results mean?
Once you know the speeds you’re getting over your internet connection, what do you do next? First, look up your plan info on your provider’s mobile app or your bill. Then, compare it to your results.
Fair warning, you probably won’t see an exact match. That’s to be expected. Here’s some additional context.
Interpreting download speeds
The download speeds that show up on your test will likely be slower than your plan speed, for a variety of reasons. If you have DSL, your speeds will be slower the further you are from neighborhood infrastructure. On satellite, cable, or fixed wireless, they’ll be slower depending on congestion in your neighborhood. With fiber, they may be slower based on factors like your device, your router, and your distance from that router.
Check multiple times a day on a few different devices to get a clear picture of whether your provider is living up to its end of the bargain.
Checking your latency
If you play online games or watch live video, you also want to pay attention to your latency. If your latency is below 20 milliseconds (ms), your experience should be perfectly smooth. If your latency is above 150 ms, you’re going to have some significant issues with lag.
Replacing an old router can reduce latency. Connecting directly to your router via Ethernet cable instead of over Wi-Fi will make a huge difference in preventing lag. Finally, you can upgrade to a type of connection with naturally lower latency, like fiber.
Diagnosing problems
If you’ve done everything you can to get the most accurate speed test and your download speeds are still way below what you expect, it could mean a few different things.
Malware: You might have malware on your device. Network worms and other malicious software hijack part of your bandwidth, but this is often the least of your worries. Run antivirus software to check for and remove malware.
Outdated hardware: You might have outdated hardware that’s incompatible with your provider’s requirements. For example, Xfinity’s gigabit services require a DOCSIS 3.1 modem. Although DOCSIS 3.0 equipment can technically get up to gigabit speeds, Xfinity doesn’t support it.
Internet service provider (ISP) issues: There might be a problem with your provider’s infrastructure. Sometimes these are just network interruptions caused by your ISP upgrading part of its network or simply doing maintenance. It could also be a more serious problem that can be fixed only by your provider. If you’ve explored the other options and are still having issues, call your ISP’s customer service.
Malfunctioning equipment: If your speed is lower than expected, but there are no problems with your internet service, there might be a problem with your equipment. Reset your modem and router by turning them off, waiting for a minute or two, then turning them back on. Try connecting to your router using an Ethernet cable instead of over Wi-Fi. If you’re already using a wired connection, try swapping out your Ethernet cable for a different one. You can also try running the speed test from a different device to see if you get the same results.
Interference: Wireless signals can experience interference from physical objects, like trees or the walls of your house, and from other electronic devices, such as your microwave or even your neighbor’s Wi-Fi router. Most of the time, this can be fixed by moving your router to a better position, but it might require changing the settings in your router’s menu.

Pro tip: Troubleshoot slow speeds
We’ve touched on the basics here, but there’s a lot more to know about fixing slow speeds. Read our expert tips to banish slow speeds. If nothing works, browse our extensive troubleshooting hub.
The terms “bandwidth” and “latency” describe an amount. Bandwidth is the amount of data you can send and receive in one second. Latency is the amount of time used by data to reach its destination and come back.
That’s the simplified version of their differences, but we’ll dive deeper into the two terms so you can better troubleshoot connection issues and get the most out of your internet service.
Is your internet feeling sluggish?
Perk up your connection using a plan with more bandwidth than you have now. Enter your zip code below to see what’s available in your area.
Bandwidth vs. latency: A deeper explanation
What is bandwidth?
Here’s the quick answer: Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data you can transfer between two points on a network.
Picture a faucet and a sink. Your bandwidth is the amount of water pouring down into your sink. Crank down on the faucet, and you get a trickle of bandwidth—you grow a head full of gray hair waiting for the sink to fill. Open the faucet all the way, and the sink fills so fast the water spills onto the floor.
As you can see, we perceive bandwidth as “speed.” The more megabits we can push through a connection in a second, the faster a file downloads or a page loads. The sink fills more quickly with the faucet wide open than when it is barely open.
Theoretically, a single cable or fiber internet connection to a home—your data faucet—supports a 10,000Mbps (10Gbps) bandwidth. But your internet provider controls that bandwidth, as does the modem and fiber optical network terminal (ONT). To get more bandwidth, you’ll want to upgrade to a “faster” plan.
Bottom line — Higher bandwidth is better
How much bandwidth do you have right now?
To find out, it’s best to run our speed test using a wired connection and compare the results to your plan’s advertised speed. If you’re on Wi-Fi, move next to the router or gateway (if you can) to get the best results from our test.
We have mobile apps you can use, too. Simply run our speed test next to the router or gateway to get the best results, and then check your numbers against your plan’s advertised speed.
What is latency?
Here’s the quick answer: Latency is the amount of time data takes to reach a remote server and return to you.
For latency, we’ll toss out the faucet analogy and imagine a road with toll booths instead. The duration of your trip squarely depends on the distance, the number of booths you must pass through, and the congestion you face along the way.
For example, there are 10 “toll booths” along the virtual road between Google and us one way, half of which are within our internet provider’s internal network. The trip is another 10 hops (toll booths) back to our device when Google replies. The completed trip to Google and back takes at least 24 milliseconds.
10 hops out + 10 hops back = 24 milliseconds. This is good latency.
Now, let’s look at satellite internet. On a good day, your data takes around 120 milliseconds to reach a satellite in space and then another 120 milliseconds to reach Google’s server here on Earth. Add another 240 milliseconds to receive Google’s response.
120 milliseconds out to space + 120 milliseconds back to Earth (Google) + 120 milliseconds out to space + 120 milliseconds back to Earth (you) = 480 milliseconds. This is bad latency.
With those two examples in mind, you’ll see a delayed action on your screen if you press a game controller button and your latency is 480 milliseconds. That’s just unplayable. But your gameplay is near flawless if the latency is only 28 milliseconds.
Latency isn’t just a gaming issue. It applies to everything you do online. Web browsers send requests to website servers every time you load a page, and the server uploads the page to your browser cache. The higher the latency, the less responsive the webpage feels.
Bottom line — Lower latency is better
How bandwidth and latency affect you
Here are a few scenarios to show how bandwidth and latency affect you daily.
Gaming
- Bandwidth: Low impact
- Latency: High impact
You don’t need a lot of bandwidth to play games online. We recommend 5Mbps or more per device for downloads and 3Mbps for uploads. If you have five people playing online simultaneously, your combined download bandwidth is around 25Mbps. However, depending on the service, you need more bandwidth to stream cloud-based games to each device—up to 25Mbps each.
Latency is vital to a good experience when you play games online—especially in fast-paced games like Fortnite and Overwatch 2. High latency manifests as lag and can cause significant delays between your input and your character’s on-screen action. In other words, you could already be dead while you’re still trying to get off a shot, but you won’t know it until your connection catches up.
Streaming
- Bandwidth: Medium impact
- Latency: Medium impact
The bandwidth you need depends on the content’s resolution and the number of devices streaming the content simultaneously. A single 4K stream averages around 25Mbps, so four devices streaming a 4K movie need at least 100Mbps of bandwidth. Plus, you’ll need extra bandwidth for all your other devices that are not streaming video.
Low bandwidth causes buffering—when the video or audio player pauses playback and waits to receive more pieces of the file before it can resume. You may also experience pixelation, as the service adjusts the stream to compensate for the narrow bandwidth (aka slow download speed).
Latency rears its head during livestreams. Your actions captured on camera appear delayed to your viewers. Latency can result from an incorrect bitrate, a longer-than-usual route to the host server, and so on.
Video chat
- Bandwidth: High impact
- Latency: High impact
Video chatting, like FaceTime or Skype, can be negatively impacted by low bandwidth and high latency. Low bandwidth affects the quality of your chat, making things hard to see. Latency causes sync issues and freezing.
Browsing
- Bandwidth: High impact
- Latency: High impact
You don’t need a lot of bandwidth to browse the internet. Web pages are mostly lightweight, so you may download around 3MB per site. However, website servers need a lot of bandwidth to upload page files to every connected device. Pages feel dial-up slow if the server is overloaded or your connection has issues.
Latency causes long page load times and makes websites feel unresponsive.
Tips for improving your connection speed
Got the internet speed blues? Here are a few things to brighten up your sad connection.
Restart your network
Sometimes you need to restart (power cycle) your network devices to refresh connections. Start by unplugging the power on your modem, gateway, or ONT. Wait 30 seconds and plug it back in.
Do the same with a standalone router or mesh system when the modem, gateway, or ONT comes back online.
Check your wired connections
A loose coax or Ethernet cable lowers your bandwidth and increases latency. Make sure coax cables are tight, and Ethernet cables have secure connections in their ports. Also, swap out damaged cables if you can—they cause speed bottlenecks and high latency too.
Check your router settings
Wi-Fi adds latency and bandwidth bottlenecks because it’s an extra translation step between you and the destination. However, a crowded channel, an incorrect channel width, and incorrect quality of service (QoS) settings are a few factors that cause unwanted slowdowns.
Check out our guide on how to improve your Wi-Fi speed for more details on what to do.
Purge unused devices
Remember that laptop you no longer use, but it’s still plugged in and connected to Wi-Fi? Chances are it’s quietly eating your precious bandwidth with a smirk as it downloads Godzilla-sized updates. Kick it off your network along with all the other data leeches you never intend to use again.
Upgrade your router
Your internet connection has a set bandwidth, but a Wi-Fi router sets the wireless bandwidth on your home network. For example, an AX1800 Wi-Fi router has less bandwidth than an AX11000 one—1,800Mbps vs. 11,000Mbps combined, respectively. Plus, you should upgrade periodically to take advantage of new technologies and higher bandwidths, especially if you upgrade smartphones every few years.
Reset your devices
The speeds you get partially depend on server-client communication. Your speed woes may have nothing to do with the internet, your modem, or your router but with the devices (clients) you use. For example, corrupted network settings will cause Wi-Fi slowdowns. The fix ranges from something simple like restarting your device to extreme measures: resetting your device back to its factory defaults.
Upgrade your internet plan
Your internet provider controls your connection’s bandwidth even if you swapped out the modem and Wi-Fi router for newer, faster models. You can’t force 1,000Mbps speeds out of a 500Mbps internet plan. To get more bandwidth, you must upgrade to a faster plan.
Not sure how much speed you need? Check out our handy speed recommendation tool to help with that.
Find a new provider
Find a new internet provider if you’ve tried everything to improve your connection, and bandwidth and latency are still an issue. Competition is fierce, and most areas have at least two great provider options.
We provide a roundup of the fastest internet providers if you’re unsure where to start. Are you a gamer? We list the best internet for gaming too, based on latency.
Our verdict: Bandwidth and latency are crucial
Bandwidth and latency have an impact on everything you do online. High bandwidth and low latency translate to the best speeds and the fastest response times—that’s what you want for your internet connection. Low bandwidth and high latency mean slow downloads, choppy streams, and delayed responses. Nobody wants that.
If you need more bandwidth than you have right now, go with a faster internet plan and a high-capacity router like an AX11000 model. Both should help keep high latencies at bay, but your total bandwidth and latency depend on the connections between the remote servers and all your devices.
If you want to know more about how internet speed works, check out our comprehensive guide to internet speed.
Does your internet plan not have enough bandwidth?
If your speeds aren’t what you need, enter your zip code to see plans and providers near you.
FAQ about bandwidth vs. latency
What’s the difference between latency and ping rate?
What type of internet connection has the lowest latency?
What’s a good latency?
How can I check my internet speed?
What is channel width?
What is Quality of Service?
Satellite internet isn’t known for being the fastest or most reliable way to connect to the internet, but there’s no need for satellite customers to suffer more than they have to. Although it’s never going to get the same performance as other connections, there are a few things you can do to get a better experience with your satellite internet.
Is your internet connection falling short of your expectations?
Enter your zip code to see what other options are available in your area.
Getting a Wi-Fi booster
A Wi-Fi booster or extender is a type of repeater that expands the range of a wireless network by rebroadcasting the signal from the router. This means your connection will bounce from your router to the repeater and then to your device, extending your network range and sidestepping obstacles to reach the farthest corners of your house.
Pro tip:
For more information on Wi-Fi extenders and how they work, read our full analysis of the Best Wi-Fi Extenders.
Most satellite internet customers connect their devices over Wi-Fi, just like with any other internet connection. Because satellite internet has relatively low download speeds and is prone to interference, it’s easy not to notice when the problem is actually your home wireless network, rather than your internet connection.
If your internet is slow or inconsistent in some rooms of your home, while consistently performing better in others, then your Wi-Fi is likely the problem. You can also try plugging a device directly into your router with an Ethernet cable.
If your Wi-Fi is the problem, a Wi-Fi extender is an easy way to boost the signal to the rest of your house. Our top pick for satellite customers is the TP-Link RE315
Troubleshoot speed problems
Wi-Fi boosters will help you fix weak signals or dead zones in your house, but they can’t increase your internet speed. If you’re getting slower than expected speeds, there are a few things you can do to troubleshoot satellite-specific issues.
Check your monthly data
Satellite plans have some of the most restrictive data caps of any internet type, so it’s very easy to go over your monthly allotment of data. Once you’ve passed your data cap, your data is deprioritized, which can drop your speed dramatically, especially during peak usage hours. If you notice a sudden drop in your internet speed, check your data to make sure you haven’t passed your limit.
Remove physical obstructions
To maintain a strong connection, your satellite dish needs to have a clear view of the south sky where your provider’s satellite is located. Physical obstructions, like a fallen branch, can block or interfere with your signal. Snow buildup on the dish itself can also interfere with your connection. Be extremely careful when removing snow or debris so as not to injure yourself or damage your dish.
Look for damage or antenna misalignment
Satellite dishes can be damaged in storms or high winds. Wind can also turn them just enough that they are no longer in alignment with the orbiting satellite. If you can see obvious damage or notice that your antenna has moved out of alignment, contact your provider to replace or realign your equipment.
Wait out bad weather
Satellite internet is uniquely vulnerable to interference from the weather. Rain, snow, extreme heat, high winds, and even sun transit can temporarily interfere with your internet connection. Unfortunately, there’s not much you can do during bad weather if you’re experiencing interference, though hybrid satellite connections like Hughesnet Fusion are slightly more resilient to this kind of interference due to having a backup network to fall back on if the other is experiencing issues.
Troubleshoot other problems
In addition to these satellite-specific issues, satellite internet can encounter the same problems as most other internet technologies. If you’re still having problems with your connection, check out some of our other troubleshooting articles for possible solutions.
Alternatives to satellite
If satellite internet doesn’t provide you with the speed or reliability that you need, there may be other options available, even in rural areas. Even if these other connections offer slower speeds than your satellite provider, there are other benefits to non-satellite internet besides speed.
5G home internet
5G home internet uses the same networks as cellular phones to deliver home internet. It’s widely available, has higher data caps than satellite, and has low monthly costs. Depending on where you live, you can get much faster speeds from 5G than you would from satellite internet. The set up is simpler too.
DSL
Much like satellite, DSL is slow and often overpriced when compared to other internet options; however, because it’s a wired connection, it has many advantages over satellite, such as lower latency, more (or unlimited) data, and a much more reliable connection. And although DSL plans can be overpriced when compared to similar speeds offered by cable or fiber, they’re still much cheaper on average than satellite.
Fixed wireless
Fixed wireless internet uses a ground-based system of antennas to connect people to the internet, especially in areas with no physical infrastructure for DSL or cable. As a wireless connection, it deals with many of the same issues as satellite, but they’re much more manageable. You’ll usually get faster speeds, more data, and less interference.
How many of these options are available in your location?
Enter your zip code to see the providers in your area.
Boosting satellite internet FAQ
How can I boost my satellite internet signal?
Can I get a Wi-Fi booster for satellite internet?
Can you get high-speed internet with a satellite dish?
Will a Wi-Fi booster speed up my satellite internet?
The terms “speed” and “bandwidth” are often used interchangeably, but they’re technically different. “Bandwidth” is the set limit of data that flows across a wired or wireless medium, while “speed” is more about how fast you can download or upload a file from start to finish. But for simplicity’s sake, internet providers always use “speed” to describe a plan’s total bandwidth.
Keep reading for a clear breakdown of the differences between internet speed and internet bandwidth—and for recommendations on internet providers with the best bandwidth for your dollar.
Explaining internet bandwidth vs. speed—the bucket analogy
The best way to explain the difference between speed and bandwidth is to use the bucket analogy.
First, picture bandwidth as a water pipe. We’ll use a wide one for fiber, a medium-sized one for cable, and a narrow one for DSL. Underneath each pipe is a huge bucket—this is your device, ready to download.
Now picture internet data as a flow of digital water, which travels at one specific speed down the pipe. An internet provider can reduce the amount of water you receive, resulting in a trickle of water no matter what pipe you use. At this rate, the bucket takes forever and a day to fill. This example represents a slow download speed, like 50 megabits per second (Mbps).
But if the internet provider increases the water to its maximum flow, the pipe determines how fast your bucket fills up with water. So, the widest pipe (fiber) fills your bucket faster than the narrowest one (DSL).
Of course, there are issues that can prevent you from filling that bucket at the rate you expect. A clogged line or a faulty pipe can reduce the flow—you name it. Similar problems apply to an internet connection, reducing your speed.
Bottom line—Bandwidth determines your speed
Internet providers advertise bandwidth as speed. A fiber connection with a 5,000Mbps bandwidth allows a single device to download a large file faster than a connection with a 140Mbps bandwidth. The more bandwidth you have, the more devices you can use simultaneously on a single internet connection.
Why are speed and bandwidth important?
Internet speed and bandwidth are important because they set the parameters for what you can do online.
Having faster speeds and higher bandwidth means you can do more online with ease, vastly reducing the chance of buffering, long load times, and other connection issues. This makes gaming, streaming, and other online activities a whole lot easier.
High bandwidth also facilitates multitasking on multiple Wi-Fi devices. It means you can efficiently support a lot of users and devices at the same time while maintaining consistent speeds and performance.
What you get with higher internet bandwidth/speeds
- Shorter load times and less buffering
- Consistent speeds across multiple internet-connected devices
- Smoother connection when streaming and playing online games
What you get with lower internet bandwidth/speeds
- Longer load times and more buffering
- Clunkier streaming, especially in HD or 4K video resolution
- Higher likelihood of speed slowdowns when multiple Wi-Fi devices are in use
Find fast internet now!
If you’re looking for an internet plan with lots of bandwidth, search your zip code below to see what’s available in your area.
How can you measure your internet speed and bandwidth?
When you sign up for an internet plan, your provider gives you a max speed that your plan can hit. That’s your bandwidth. It represents what you can accomplish when your Wi-Fi is firing on all cylinders.
Speed test results aren’t static the same way bandwidth is—the numbers tend to vary day to day based on a range of factors, including your internet connection type, your router, the number of people on your Wi-Fi, and even the location of your router in your home.
Best internet plans for speed and bandwidth
| Plan | Price | Speed | Order online |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xfinity 300 Mbps | Check Xfinity for price* | 300Mbps | |
| Spectrum Internet Premier w/ Spectrum Advanced | $60/mo.† for 12 mos. | Up to 500Mbps (wireless speeds may vary) | |
| Verizon Internet 300/300 | $39.99–$49.99/mo.‡ | 300Mbps | View Plans |
| Google Fiber 1 Gig | $70.00/mo.§ | Up to 1,000Mbps | View Plans |
| AT&T Internet 5000 | $250.00/mo.║ | Up to 5,000Mbps |
Read disclaimers.
Internet providers have been racing to raise their speeds so much over the past few years that an internet plan that once seemed fast nowadays might actually be on the slower side. We talk at length about internet speed in our Fastest Internet Providers report, which highlights the speediest and breeziest internet providers in the country.
Still, most people don’t need the fastest internet to be happy—according to one report, only 12% of internet users in North America have gigabit speeds on their home internet plans.1
Bandwidth really becomes an issue only when your speeds aren’t fast enough to meet your daily needs. If you’re shopping for an internet plan and trying to figure out the best speeds, you should think about not just what you do online, but also what your roommates or family members do. The more people you have on your Wi-Fi, the bigger strain that puts on your bandwidth.
Which types of internet have the most bandwidth?
| Internet type | Bandwidth capacity | Max speeds | View providers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber | Very high | 100–10,000 Mbps | View Fiber Providers |
| Cable | High | 25–1,200 Mbps | View Cable Providers |
| 5G | Medium | 35–1,000 Mbps | View 5G Providers |
| DSL | Low | 1–140 Mbps | View DSL Providers |
| Satellite | Very low | 25–100 Mbps (throttled when you hit data cap) | View Satellite Providers |
The type of internet you have plays a central role in determining the amount of bandwidth you can get from your internet plan. Different types of internet providers have certain technical limits on the amount of throughput they can deliver.
It’s likely you can get relatively fast download and upload speeds from your internet provider—our own speed-test data shows that internet speeds have been going up since the pandemic started in 2020. Still, some internet types remain relatively sluggish, especially in rural areas.
Take a look below to see how different internet types rate in terms of speed and bandwidth.
Comparing bandwidth for different internet types
Fiber-optic internet gives you the most bandwidth and the fastest internet speeds, with internet plans topping out at a ridiculous 10,000 Mbps. Nobody really needs internet that fast (not yet, at least), but fiber also speeds ahead of other internet types because it has symmetrical upload speeds.
Symmetrical uploads mean you can get up to gigabit-speed throughput on uploads as well as downloads, vastly boosting your ability to hold video calls, upload large files to the internet, and post to social media.
Cable internet is often just as fast as fiber internet, at least for download speeds. Cable internet has much slower upload speeds compared to fiber, and it also can’t deliver impressive (albeit unnecessary) multigigabit speeds. But for most people, it’s as good as it gets for bandwidth.
5G internet doesn’t have the same impressive bandwidth as fiber or cable, but it’s much faster than more antiquated internet types like DSL. A relatively new technology, 5G can be found mostly in urban areas through cellular providers Verizon and T-Mobile.
The internet connection draws entirely from 5G wireless networks, which makes it very fast but also slightly unstable—so your speeds can vary considerably throughout the day, and you may experience occasional disconnects.
DSL internet is a somewhat outdated internet service that seems slower and slower as cable and fiber providers increasingly raise their speeds. DSL maxes out at 140 Mbps, but many DSL users experience much slower speeds due to the technical limitations of a DSL connection.
DSL’s copper wire connections deteriorate in strength as the user gets farther away from a central server, which makes for particularly slow connections in rural areas, suburbs, and the outskirts of cities.
Satellite internet is the slowest type of internet you can get. A satellite connection draws from a signal literally beaming down from space, which makes for much higher latency and vastly limits the amount of bandwidth you can get.
However, Starlink’s emerging satellite service has much faster speeds than traditional satellite providers HughesNet and Viasat. That’s because Starlink relies on a larger number of satellites, which orbit at a lower altitude.
Pro tip:
Are you dealing with a slow internet connection? Take a look at our tips to improve your internet speed.
What internet activities use the most bandwidth?
| Online activity | Recommended bandwidth |
|---|---|
| Checking email | 1 Mbps |
| Making Zoom calls (1:1 only and without video) | 1.5 Mbps |
| Playing online games | 5 Mbps |
| Streaming music | 10 Mbps |
| Videoconferencing with groups | 25 Mbps |
| Streaming video in HD or 4K on one or two devices | 25–50 Mbps |
| Streaming video in 4K on several devices | 100–500 Mbps |
| Streaming video in 4K while playing a video game online and making a video conference call all at the same time, while your roommate does the same thing in the next room | 1,000 Mbps |
| Hosting a livestream | 500–1,000 Mbps |
Most online activities take up only a small amount of bandwidth. But you use a lot more bandwidth to make video calls, stream video, or host livestreams. And all of these demands on your internet speed really start to add up if you’re sharing an internet connection with other users.
To play it safe, we recommend setting aside at least 25 Mbps worth of bandwidth for every internet user in your household. So if you live with three other people, then an internet plan with max speeds of 100 Mbps should be fine.
However, definitely consider a faster plan—say, 50 Mbps per person—if you regularly do high-bandwidth activities like streaming movies in 4K or hosting livestreams on Twitch.
Search your zip code to find high-bandwidth internet in your area.
Sources
- OpenVault, “Broadband Insights Report—Q4 2021,” March 2022. Accessed March 2, 2022.
Disclaimers
Best internet plans (return to top)
* For 12 months, no term contract. Restrictions apply. Autopay w/ stored bank account and paperless billing req’d. Taxes and fees extra and subj. to change. Reduced speeds after 30 GB of usage/line. Data thresholds may vary.
† Limited time offer; subject to change; new residential customers only (no Spectrum services within past 30 days) and in good standing with Spectrum. Taxes and fees extra in select states. SPECTRUM INTERNET: Standard rates apply after promo period. Additional charge for installation. Speeds based on wired connection. Actual speeds (including wireless) vary and are not guaranteed. Gig capable modem required for Gig speed. For a list of Gig capable modems, visit spectrum.net/modem. Services subject to all applicable service terms and conditions, subject to change. Not available in all areas. Restrictions apply.
‡ w/ Auto Pay. Available in select areas.
§ Terms and Conditions: Plus taxes and fees. Service not available in all areas. If you live in an apartment or condo, Google Fiber’s ability to construct and provide Fiber is subject to the continued agreement between Google Fiber and the property owner. Upload/download speed and device streaming claims are based on maximum wired speeds. Actual Internet speeds are not guaranteed and may vary based on factors such as hardware and software limitations, latency, packet loss, etc.
║ Price after $5/mo Autopay & Paperless bill discount (w/in 2 bills). Plus taxes & fees. Internet speed claims represent maximum network service capability speeds and based on wired connection to gateway. Actual customer speeds may vary based on a number of factors and are not guaranteed. For 5GIG speed, single device wired speed maximum 4.7Gbps. For more information, go to www.att.com/speed101.
HighSpeedInternet.com’s most recent internet speed test data shows the national average internet speed in 2024 was 214Mbps—a 9% year-over-year increase from the previous year’s 196Mbps.
While many Americans now have access to high-speed fiber and 5G broadband, rural areas and underserved communities still fall behind, deepening the digital divide.
Although speeds continue to rise, our Fastest Internet Provider Report shows that the pace of improvement is slowing. Without significant infrastructure advancements and expansion, we could eventually hit a plateau for increasing speeds.
We’ll go over internet speeds across the U.S., highlighting the fastest and slowest states, and examine how these speeds impact everyday activities—from work and school to gaming and streaming. We’ll also discuss the steps being taken to ensure faster internet access in the future.

Internet speeds across America
The average internet speed in the U.S. has reached 214Mbps, reflecting a 9% increase year-over-year from 2023’s 196Mbps.
Several nationwide initiatives, alongside private sector expansion, contributed to these rising speeds and helped bridge the digital divide: The Internet for All program was driving major broadband investments, particularly in underserved areas, while the FCC’s restoration of net neutrality aimed to ensure fairer access and prevent throttling. On top of that, updated broadband benchmarks helped set clearer expectations for internet service providers (ISPs), pushing them to deliver faster and more reliable service.
The fastest internet speeds are found in densely populated coastal states, like Delaware (246.95Mbps), Maryland (238.26Mbps), and New Jersey (235.67Mbps). Strong fiber networks and competition among providers keep speeds high.
Meanwhile, more rural states like Idaho (124.57Mbps), Montana (129.73Mbps), and Alaska (125.09Mbps) get about half the speed due to limited high-speed options and infrastructure.

States with the fastest and slowest internet speeds
To get a clearer picture of national internet access, we ranked states by speed. When compared against the national average, 15 states have speeds above the national average download speeds, and 36 states have speeds below the national average, meaning more states have substandard internet speeds than we could expect, likely due to gaps in access to high-speed broadband networks.
States with the fastest internet speeds
The fastest states for internet in 2025 are largely concentrated in the Northeast and Southeast, where dense infrastructure and major provider investments have driven speeds higher for more people. In fact, 70% of the top-performing states are in these regions.
Setting the new gold standard, these states all have internet download speeds of 220 or more, with Delaware taking the top spot at 246.95 Mbps.

States with the slowest internet speeds
How much do internet speeds vary across the slowest states? At rank 10, Vermont comes in at 166 Mbps, while Idaho—the slowest—comes just 124.57 Mbps, nearly half the average of the fastest states, which reach around 225 to 250 Mbps.

Since broadband expansion is more difficult in rural and mountainous areas, states in the West and Midwest make up most of those with the slowest speeds. Even though demand is lower in these areas, better internet connectivity remains crucial for economic growth, education, and remote work opportunities.
The digital divide: How internet speed varies by region and demographics
High-speed internet access isn’t just about technology—it’s shaped by where you live, what you earn, and the available infrastructure.
Cities with denser populations enjoy faster, more reliable internet thanks to higher demand and more investment from providers. In contrast, remote regions face slower speeds due to the high expansion costs, challenging terrain, and smaller customer bases.
Many lower-income households, even in metro areas, rely on slower, budget-friendly plans—or lack broadband access altogether. Everyday activities, like shopping and online banking, might be lightning quick to accomplish for some but may take others much longer—if they can at all.
The internet speeds you need
For smooth streaming, online gaming, remote work and school, and telehealth, you’ll likely need at least 25Mbps. While many activities don’t require that much speed, it’s important to also consider latency and how bandwidth is shared across multiple devices.
High-performance tasks require more speed than basic activities. For example, HD streaming needs 5 to 10Mbps, but 4K streaming requires 25Mbps or more. Online gaming works best with at least 20Mbps, but a low ping rate is just as crucial. Remote work, school, and telehealth services typically require 10 to 25Mbps. If you want to do multiple of these activities at once, you’ll need even faster speeds to accommodate extra tasks.
When more people and devices are online at once, performance can slow down, especially during peak usage times, compared to the quiet hours of the night when fewer people are online.
Areas with average speeds well above 200Mbps (like California, Colorado, and New Jersey) are more than capable of doing high-demand activities like 4K streaming, online gaming, and remote work regularly with little-to-no trouble.
However, states with lower speeds (such as Idaho, Montana, and Alaska) may struggle with these activities, particularly in rural regions where speeds can be much slower, impacting performance and reliability.
For more information about how much internet speed you need for your regular activities, check out our full guide to internet speed.
Looking ahead: What the US is doing to invest in faster internet speeds
As we discussed in our Fastest ISP Report, as internet demand continues to grow, providers must invest in next-generation technology to boost speeds nationwide.
The rollout of DOCSIS 4.0 brings multi-gigabit speeds to cable internet users, which will improve both download and upload capabilities. Meanwhile, XGS-PON fiber networks show much better acceleration and deployment, expanding access to symmetrical gigabit speeds in urban and suburban areas.
Meanwhile, federal and state broadband initiatives (for example, the BEAD program) are working to close the digital divide by funding broadband expansion to rural and underserved areas.
Conclusion and key takeaways
As internet speeds continue to rise across the U.S., disparities remain between the speedy urban and suburban areas and the slower remote and rural areas. While the national average download speed has reached 214Mbps, driven by fiber expansion and 5G broadband, most states still fall below this benchmark. Coastal states benefit from strong infrastructure and competition, while rural and mountainous regions struggle with slower speeds due to limited broadband access.
Looking ahead, investment in next-gen technologies like DOCSIS 4.0 and XGS-PON fiber will help raise overall speeds. In addition, federal and state initiatives will help expand broadband access to underserved communities, bringing better, more reliable, and faster connections to more Americans.
With these advancements and efforts, 2025 looks to be a transformative year for internet access and performance across the U.S.
Top 10 states with the fastest internet speeds
| Rank | State | Average download speed |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delaware | 246.95Mbps |
| 2 | Maryland | 238.26Mbps |
| 3 | New Jersey | 235.67Mbps |
| 4 | Connecticut | 233.88Mbps |
| 5 | Florida | 232.80Mbps |
| 6 | Virginia | 230.49Mbps |
| 7 | Rhode Island | 227.10Mbps |
| 8 | Texas | 225.74Mbps |
| 9 | California | 223.59Mbps |
| 10 | Nevada | 220.91Mbps |
Top 10 states with the slowest internet speeds
| Rank | State | Average download speed |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Idaho | 124.57 |
| 2 | Alaska | 125.09 |
| 3 | Montana | 129.73 |
| 4 | Hawaii | 146.07 |
| 5 | Wyoming | 147.19 |
| 6 | Iowa | 150.74 |
| 7 | Minnesota | 164.68 |
| 8 | South Dakota | 164.71 |
| 9 | West Virginia | 164.85 |
| 10 | Vermont | 166.40 |
Average internet download speeds of all states
| State | Average download speed | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 191.88 | 31 |
| Alaska | 125.09 | 50 |
| Arizona | 200.64 | 24 |
| Arkansas | 194.82 | 29 |
| California | 223.59 | 9 |
| Colorado | 219.79 | 11 |
| Connecticut | 233.88 | 4 |
| DC | 182.39 | 37 |
| Delaware | 246.95 | 1 |
| Florida | 232.80 | 5 |
| Georgia | 194.98 | 28 |
| Hawaii | 146.07 | 48 |
| Idaho | 124.57 | 51 |
| Illinois | 201.12 | 22 |
| Indiana | 206.46 | 18 |
| Iowa | 150.74 | 46 |
| Kansas | 186.88 | 34 |
| Kentucky | 183.31 | 35 |
| Louisiana | 203.11 | 21 |
| Maine | 173.23 | 40 |
| Maryland | 238.26 | 2 |
| Massachusetts | 218.54 | 12 |
| Michigan | 193.19 | 30 |
| Minnesota | 164.68 | 45 |
| Mississippi | 187.07 | 33 |
| Missouri | 196.43 | 27 |
| Montana | 129.73 | 49 |
| Nebraska | 177.37 | 38 |
| Nevada | 220.91 | 10 |
| New Hampshire | 217.06 | 14 |
| New Jersey | 235.67 | 3 |
| New Mexico | 173.62 | 39 |
| New York | 208.05 | 17 |
| North Carolina | 197.61 | 26 |
| North Dakota | 171.03 | 41 |
| Ohio | 188.20 | 32 |
| Oklahoma | 216.91 | 15 |
| Oregon | 209.69 | 16 |
| Pennsylvania | 204.66 | 20 |
| Rhode Island | 227.10 | 7 |
| South Carolina | 199.35 | 25 |
| South Dakota | 164.71 | 44 |
| Tennessee | 205.07 | 19 |
| Texas | 225.74 | 8 |
| Utah | 218.06 | 13 |
| Vermont | 166.40 | 42 |
| Virginia | 230.49 | 6 |
| Washington | 201.11 | 23 |
| West Virginia | 164.85 | 43 |
| Wisconsin | 183.11 | 36 |
| Wyoming | 147.19 | 47 |
Consult our 2025 methodology for more information about the data we used for this article.
-
Fastest tested speeds
- Fastest fiber-optic speeds according to our speed test
- Very limited availability
- Speeds: 1,000–8,000Mbps
- Prices: $70.00–$150.00/mo.*
-
Lowest latency
- Lowest latency rates
- Expensive gigabit plan
- Speeds: 300–2,300Mbps
- Prices: $49.99–$109.00/mo.† w/ Auto Pay
-
Best fiber price
- No extra fee for installation or equipment
- Limited availability
- Speeds: 940Mbps
- Prices: $75.00/mo.‡
-
Fast advertised speeds
- Multi-gigabit internet plans
- Unnecessarily fast speeds on fastest plans
- Speeds: 25–5,000Mbps
- Prices: $55.00–$180.00/mo.§
Read disclaimers.
Symmetrical internet is the great equalizer. On a symmetrical internet plan, your upload speeds are just as fast as your download speeds.
Most internet connections have much faster download speeds than upload speeds. Let’s say your cable internet plan gives you 100Mbps download speeds. In that case, your upload speeds would be just 10Mbps—or even less.
A symmetrical plan gives you a big upload boost. So if your download speeds are 100Mbps, your upload speeds are also 100Mbps.
Wait, what are upload and download speeds again?
Download speeds measure how long it takes to pull stuff from the internet. Whether you’re opening an email, streaming a movie on Netflix, or updating your favorite video game, you’re downloading content—it’s what we spend most of our time doing online.
Upload speeds measure how long it takes to send stuff to the internet. It means sending an email, posting to social media, or making a video call with a coworker. Uploading also includes bigger undertakings like livestreaming and playing around in the metaverse, which require a lot more bandwidth.
Symmetrical internet sounds awesome. So how can I get it?
You can get symmetrical speeds with fiber internet, which is mostly available in urban areas but also some rural communities.
Fiber’s fast speeds and symmetrical uploads make it the most efficient and reliable internet type, giving you a crucial leg up for remote work and online entertainment.
Want to know more? Here’s a quick breakdown of what symmetrical internet is, why it’s good, and how to get it.
Best symmetrical internet plans
| Plan | Download / upload speed | Prices | Order online | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Core 1 Gig | 1,000Mbps / 1,000Mbps | $70.00/mo.** | View Plan |
|
| Verizon Fios 1 Gig | Up to 940Mbps / Up to 880Mbps | $89.99/mo.† w/ Auto Pay | View Plan |
| CenturyLink Fiber Internet | 940Mbps / 940Mbps | $75.00/mo.‡ | ||
| AT&T Internet 5000 | 5,000Mbps / 5,000Mbps | $180.00/mo.*** |
See disclaimers at bottom of page.
The best symmetrical internet plans come from fiber internet providers—which makes sense, considering that fiber is the only way you can get symmetrical internet.
These plans give you incredibly fast upload speeds, ensuring that you have all the bandwidth you could ever want to attend Zoom meetings, post content online, and host livestreams. The plans will also make it possible for you to share your Wi-Fi with a large number of other users without worries over a slow connection or long buffering times.
Pro tip:
Fiber internet is the best internet, in our opinion. Figure out why by looking at fiber internet speeds, prices, and plans.
Why is symmetrical internet important?
Symmetrical internet is important because it gives you the fastest speeds possible to do upload-heavy tasks.
It’s also important because it gives you a huge amount of upload bandwidth to support a large number of users who are all sharing the same Wi-Fi connection. If you live with a lot of roommates or family members, a symmetrical connection ensures fast speeds and top performance even when a bunch of people are streaming, gaming, and Zooming on multiple devices at the same time.
Activities that benefit from symmetrical internet:
- Livestreaming
- Posting frequently to TikTok, Instagram Reels, and YouTube
- Frequently attending Zoom or other video conference meetings
- VR and AR gaming and activities
Why does fiber internet have symmetrical speeds?
Fiber has symmetrical speeds because it has a much larger capacity to deliver data compared to other internet types.
Fiber provides a connection using bundled strands of fiber-optic cable. Photon signals bounce through the cables at the speed of light (or at least something close), carrying vast amounts of data. Fiber-optic cable is often newer than the copper wiring of cable and DSL internet, and it isn’t susceptible to electromagnetic interference, adding to its capabilities.
Fiber is the only type of internet that gives you symmetrical speeds right now. Cable internet may catch up in a few years as tech standards evolve, but right now, fiber is really the way to go.
Do you need symmetrical internet speeds?
Most people don’t need symmetrical internet speeds. But they’re nice to have, and those speeds will especially make your life a lot easier if you have any job or passion that requires extensive time on the internet.
Jobs that benefit from symmetrical internet:
- Social media influencer
- Content creator
- Professional gamer
- Filmmaker who frequently posts content online
Of course, the majority of people in the United States don’t have symmetrical internet speeds and many are doing just fine.1 Most of what we do online involves downloading data rather than uploading it, so internet providers haven’t felt a great demand to up their uploads—but times may be changing.
There’s a rising demand for fast uploads, thanks to the drastic rise of remote working, increasingly ubiquitous internet connectivity, and a greater push for video content on social media (shoutouts to Instagram Reels and TikTok). And while you don’t need speedy uploads, you greatly benefit from having them.
Long story short—Get fiber internet for symmetrical speeds (and for lots of other great reasons too)
Fiber internet is the only internet that gets you symmetrical speeds. So if you want symmetrical internet, then get a fiber plan if it’s available in your area.
But also, it just so happens that fiber is the best type of internet you can get, and not just because of the upload speeds. Compared to cable or DSL internet, fiber gives you an incredibly fast and reliable connection, packs in more Mbps for your dollar, and often comes with extra perks like free equipment and unlimited data.
If you can get fiber internet, we say go for it.
FAQ about symmetrical internet
Why don’t other internet connection types have symmetrical internet?
Disclaimers
Symmetrical internet providers (return to top)
Data effective 10/7/24. Offers and availability may vary by location and are subject to change.
*Plus taxes and fees. Upload/download speed and device streaming claims are based on maximum wired speeds. Actual Internet speeds are not guaranteed and may vary based on factors such as hardware and software limitations, latency, packet loss, etc.
† Verizon
- Price per month without select 5G mobile plans.Consumer data usage is subject to the usage restrictions set forth in Verizon’s terms of service; visit: https://www.verizon.com/support/customer-agreement/ for more information about 5G Home and LTE Home Internet or https://www.verizon.com/about/terms-conditions/verizon-customer-agreement for Fios internet.
- Available in select areas only. Price per month without select 5G mobile plans. Consumer data usage is subject to the usage restrictions set forth in Verizon’s terms of service; visit: https://www.verizon.com/support/customer-agreement/ for more information about 5G Home and LTE Home Internet or https://www.verizon.com/about/terms-conditions/verizon-customer-agreement for Fios internet.
‡Speed may not be available in your area. Maximum download/upload speed of up to 940 Mbps via a wired connection. Paperless billing required. Taxes and fees apply. Offer details. Offer includes professional installation at customer’s eligible location.
§Speeds based on wired connection. Actual speeds may vary. For more info, go to www.att.com/speed101.
Price after $5/mo Autopay & Paperless bill discount (w/in 2 bills). Plus taxes & fees. Monthly State Cost Recovery Charge in TX, OH, NV applies. One time install chrg may apply. Ltd. avail/areas. Call or go to www.fiber.att.com to see if you qualify.
Price after $5/mo Autopay & Paperless bill discount (w/in 2 bills). Plus taxes & fees. Monthly State Cost Recovery Charge in TX, OH, NV applies. Ltd. availability/areas.
Best symmetrical internet plans (return to top)
**Terms and Conditions: Plus taxes and fees. Service not available in all areas. If you live in an apartment or condo, Google Fiber’s ability to construct and provide Fiber is subject to the continued agreement between Google Fiber and the property owner. Upload/download speed and device streaming claims are based on maximum wired speeds. Actual Internet speeds are not guaranteed and may vary based on factors such as hardware and software limitations, latency, packet loss, etc
† Verizon
- Price per month without select 5G mobile plans.Consumer data usage is subject to the usage restrictions set forth in Verizon’s terms of service; visit: https://www.verizon.com/support/customer-agreement/ for more information about 5G Home and LTE Home Internet or https://www.verizon.com/about/terms-conditions/verizon-customer-agreement for Fios internet.
- Available in select areas only. Price per month without select 5G mobile plans. Consumer data usage is subject to the usage restrictions set forth in Verizon’s terms of service; visit: https://www.verizon.com/support/customer-agreement/ for more information about 5G Home and LTE Home Internet or https://www.verizon.com/about/terms-conditions/verizon-customer-agreement for Fios internet.
‡Speed may not be available in your area. Maximum download/upload speed of up to 940 Mbps via a wired connection. Paperless billing required. Taxes and fees apply. Offer details. Offer includes professional installation at customer’s eligible location.
***Price after $5/mo Autopay & Paperless bill discount (w/in 2 bills). Plus taxes & fees. Monthly State Cost Recovery Charge in TX, OH, NV applies. Ltd. availability/areas.
Download speeds of 25Mbps are no longer fast enough to fully participate in modern society, according to a report adopted today by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Instead, the agency has announced a new speed benchmark of 100Mbps for download speeds and 20Mbps for upload speeds for fully wired connections. In agency shorthand, that’s 100/20.
How fast is 100Mbps?
Download speeds of 100Mbps are fast enough to play games online, stream shows and movies in HD, and attend online meetings. They can support a household with beteween five and seven users.
Find out how much speed you need.
Future broadband speed goals
In addition to setting new standards for broadband deployment today, the commission set a future goal for download speeds of 1,000Mbps (1Gbps) with upload speeds of 500Mbps (1,000/500). It did not set a date for reaching the new speed targets, but several national fiber internet providers such as AT&T, Frontier, Google Fiber, Verizon, and Quantum Fiber already offer those speeds in certain areas.
The previous FCC Broadband standard of 25Mbps for download speeds and 3Mbps for upload speeds was set in 2015.
With the updated standards, the FCC’s assessment is that high-speed internet was not being deployed “in a reasonable and timely fashion” as of December of 2022. The report accounts for all Americans, including those in rural areas and people living on Tribal lands.
Who has access to high-speed internet?
According to the latest broadband map published by the FCC, 92.11% of households in the U.S. have access to fixed broadband of 100/20 speeds now, and 94.92% have access to fixed broadband speeds of 25/3. The data is imperfect for a variety of reasons—including that it comes primarily from internet providers themselves—but it’s much better now than it has been for the past several years.
It’s important to note that the speed gap is a lot greater in some regions than it is overall. For example, 95% of people in Idaho have access to 25Mbps today, according to map data, but only 83% have 100Mbps speeds. Rural states are the worst off, and they stand to benefit the most.
Looking for an easy way to test and track your internet speed anywhere?
Download our free, easy-to-use speed test app for quick and reliable results.
According to the 2022 data cited in the report, about 24 million Americans don’t have access to high-speed internet at the 100/20 level. About 45 million don’t have access to either 100/20 speeds or the 5G standard of 35/5.
Americans living in rural areas suffer the slowest speeds out there.
“We are particularly concerned that those living in rural areas are almost four times more likely than average Americans not to have access to advanced telecommunications capability,” the FCC report reads. “Those living on Tribal lands are almost three times more likely than average Americans not to have access to advanced telecommunications capability.”
Average cost of high-speed internet
According to the March 14 report, the average cost of a home internet plan with speeds of at least 100Mbps is $100 per month. That’s $70 more per month than the current federal subsidy of $30 per month. The data was not definitive.
Dissenting opinions among FCC commissioners
FCC Commissioners Brendan Carr and Nathan Simington voted against adopting the report. Carr’s reasoning was that the 2022 data was too old to be useful. He also thinks the new standard is an overreach by the FCC that goes beyond what lawmakers in the U.S. Congress intended.
Simington was pleased the new report mentions latency and jitter, but criticized the lack of inclusion of satellite internet in the new standard. He also criticized the long-term goal of 1,000/500, calling it unnecessary. It could lead to “a generation of wasteful spending,” he said.
Two other commissioners and Chairman Jessica Rosenworcel voted in favor of the change.
Commissioner Anna Gomez, who often addressed the audience in the Spanish language, was one of the approvers.
“Updating the FCC’s benchmark to 100/20Mbps reflects the reality of the market and consumer needs in today’s increasingly connected world,” she said. “But, more must be done to connect the 24 million consumers currently not served by high-speed broadband.”
Gomez, like other commissioners, also spoke about failure by the U.S. Congress to allocate additional funding for the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP). Learn more about the program to provide cheap internet to low-income families in our expert resource library.
What’s next for the FCC?
The agency plans to use its new benchmarks to decide where to spend taxpayer money on broadband infrastructure projects. Usually, these projects are private-public partnerships, meaning some of the money for construction comes from taxes and some comes from internet service providers. When projects are complete, the internet providers own the infrastructure.
The only actionable statement in the report is that deployment of new speeds “must occur in rapid fashion so as to not leave large groups of Americans without access to broadband.”
The full FCC report on the new speed standards is available on the agency’s website.
Staff Writer Peter Christiansen contributed to this article.





